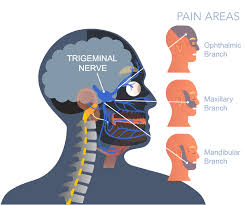
Chronic Back Pain Solutions: The Role of MRI in Treatment
Do X-rays help diagnose back pain? How important is MRI in treating chronic back pain?
X-RAY APPROACH
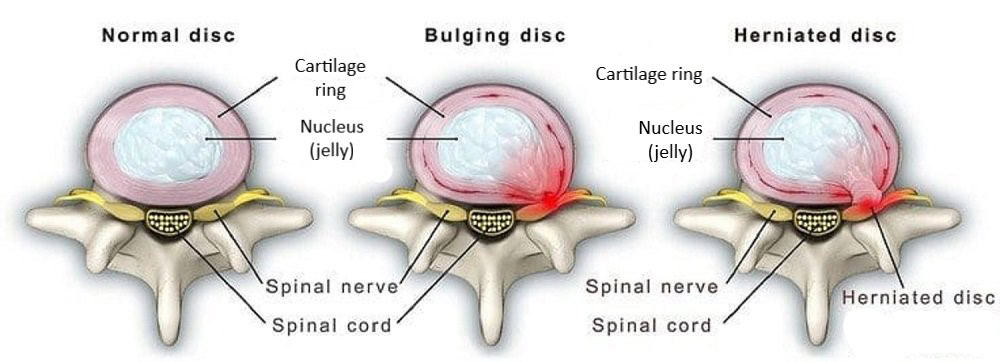
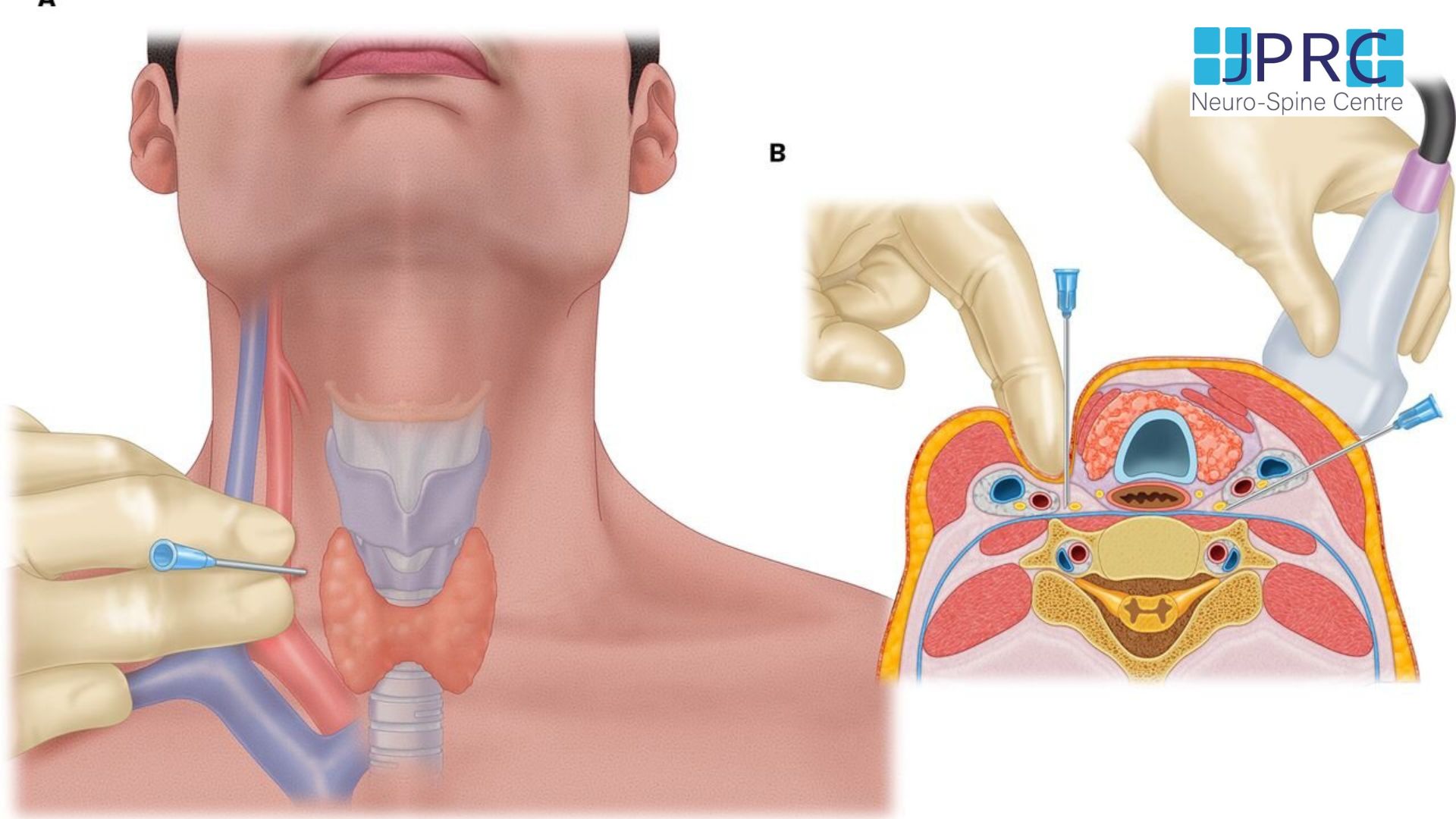
Common imaging techniques can acquire images of bones and soft tissues using these. X-rays help diagnose back pain. They detect spine fractures, tumors, and degenerative changes well.
X-rays can rule out serious illnesses or identify ruptured discs or spinal misalignments in back pain patients. However, X-rays have limits. They don't show muscles, ligaments, and nerves, which are typically involved in chronic back pain.
MRI ADVANTAGE
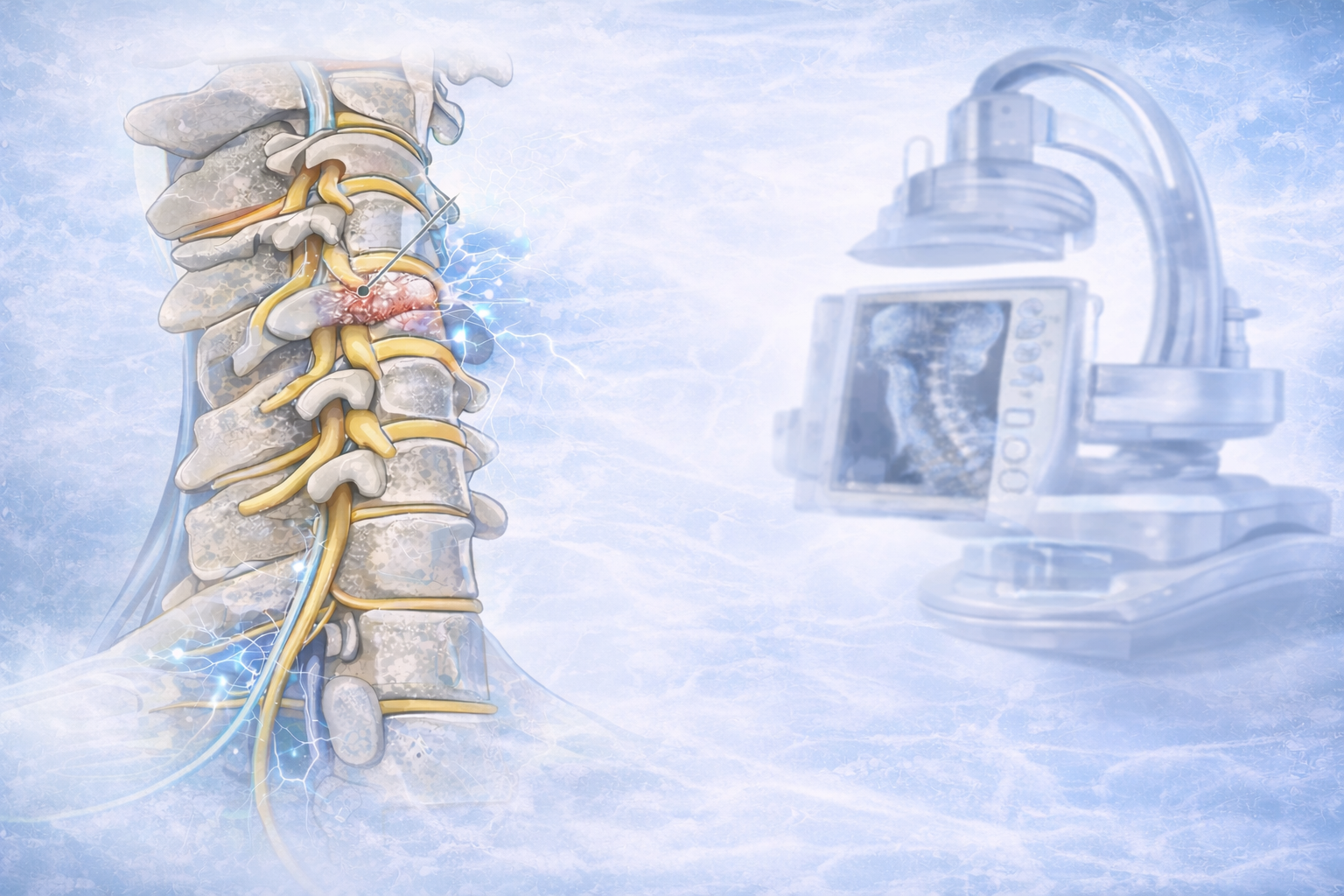
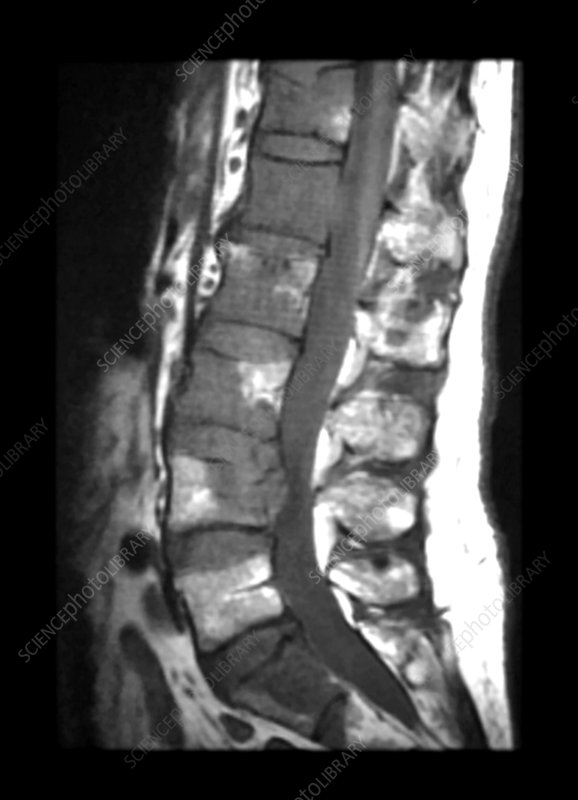
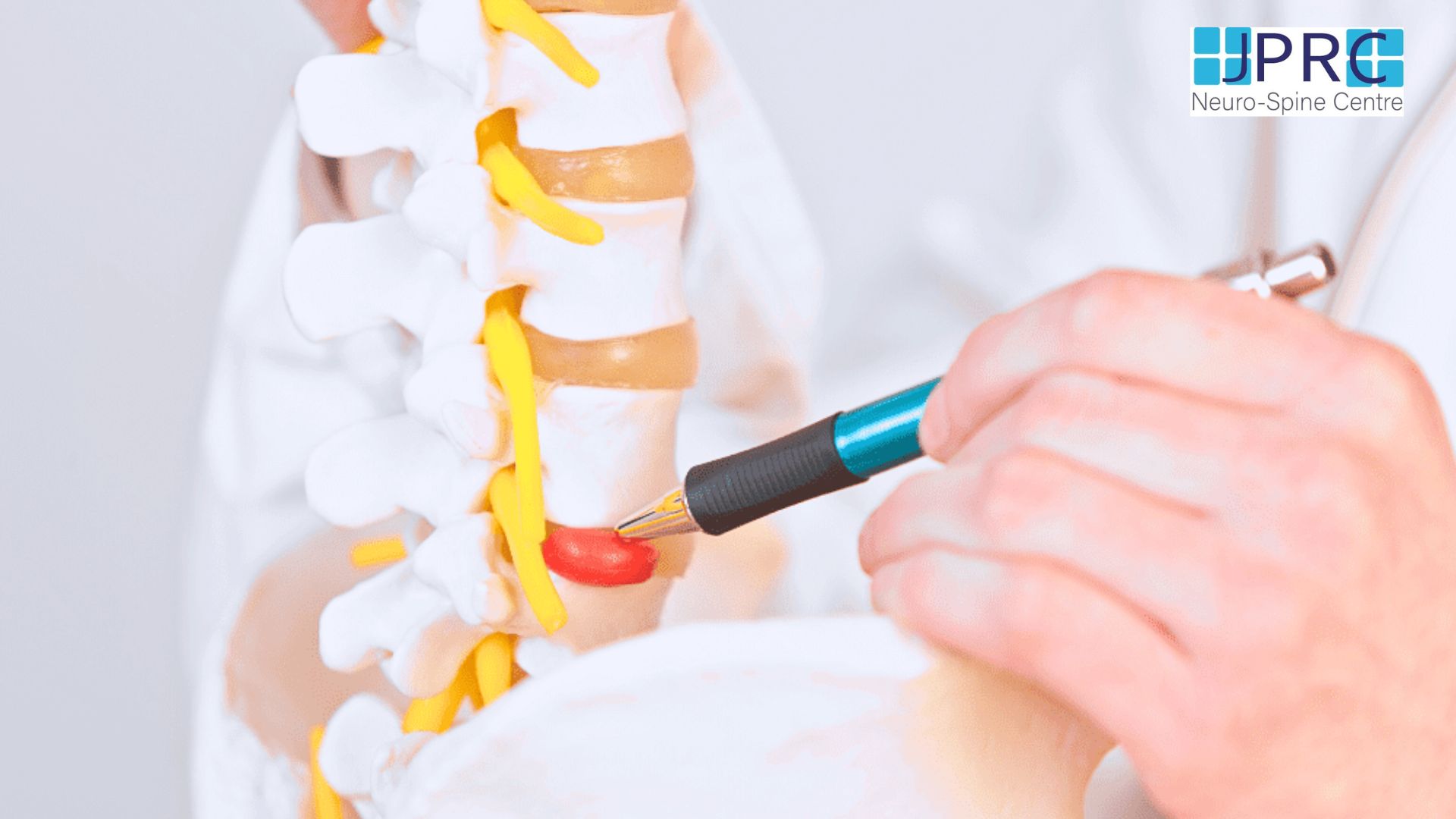
Chronic back pain diagnosis and therapy benefit from an MRI. MRIs employ a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to provide detailed images of the body's bones and soft tissues, unlike X-rays, which use ionizing radiation.
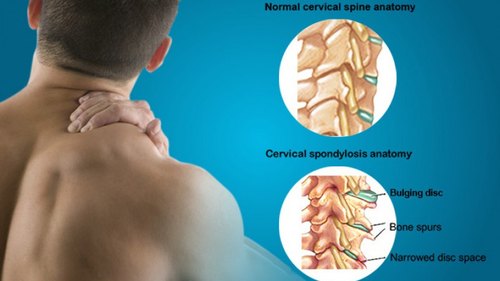
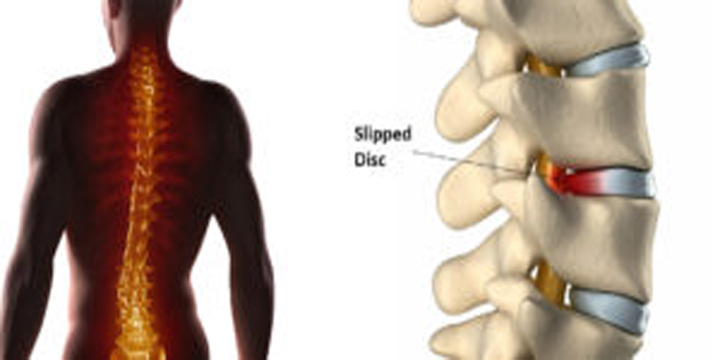
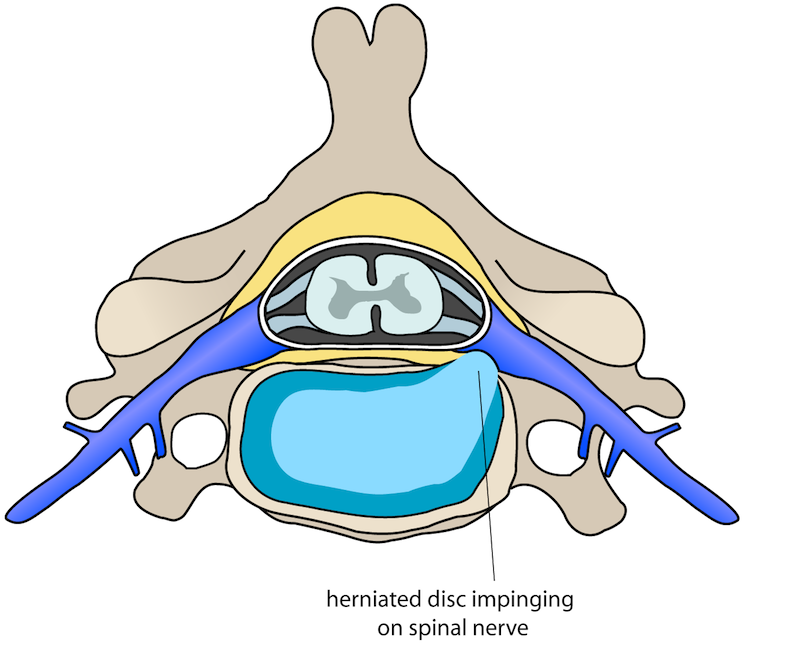
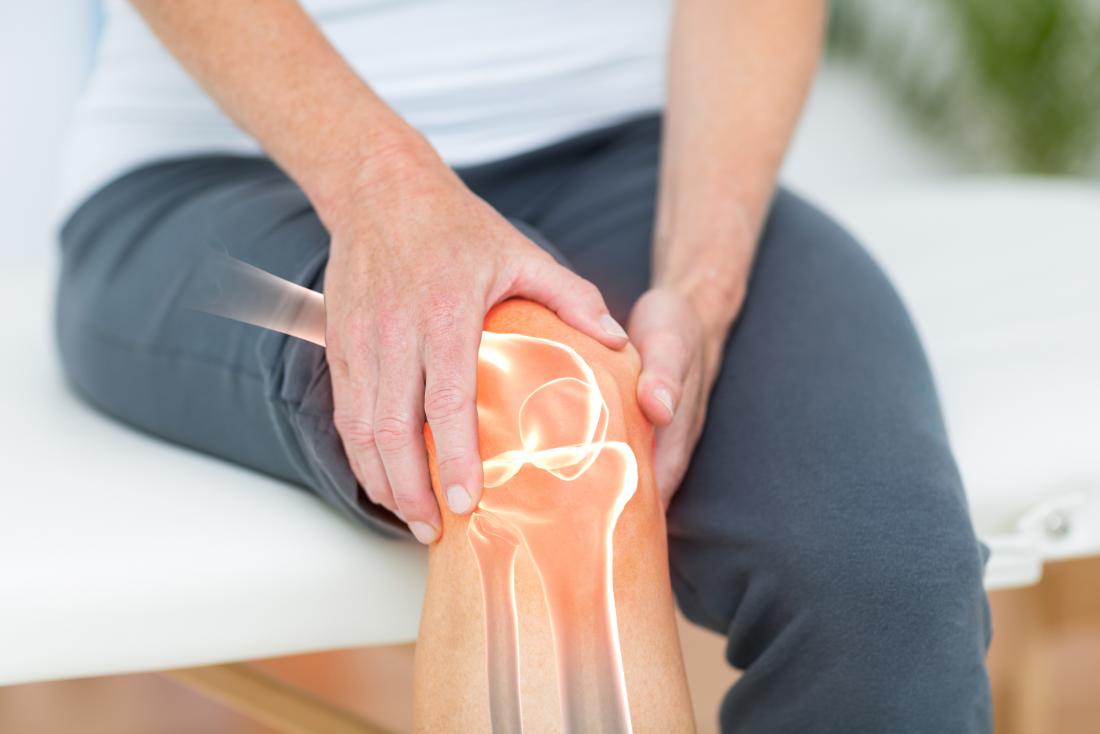
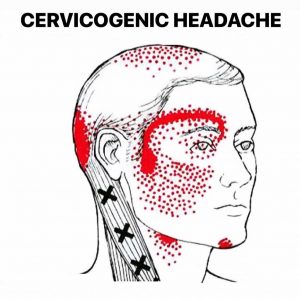
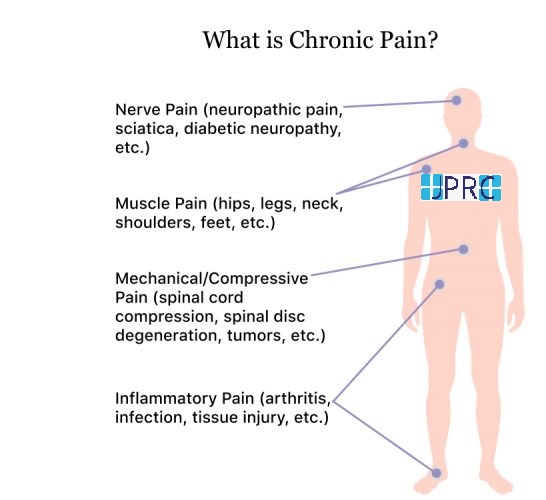
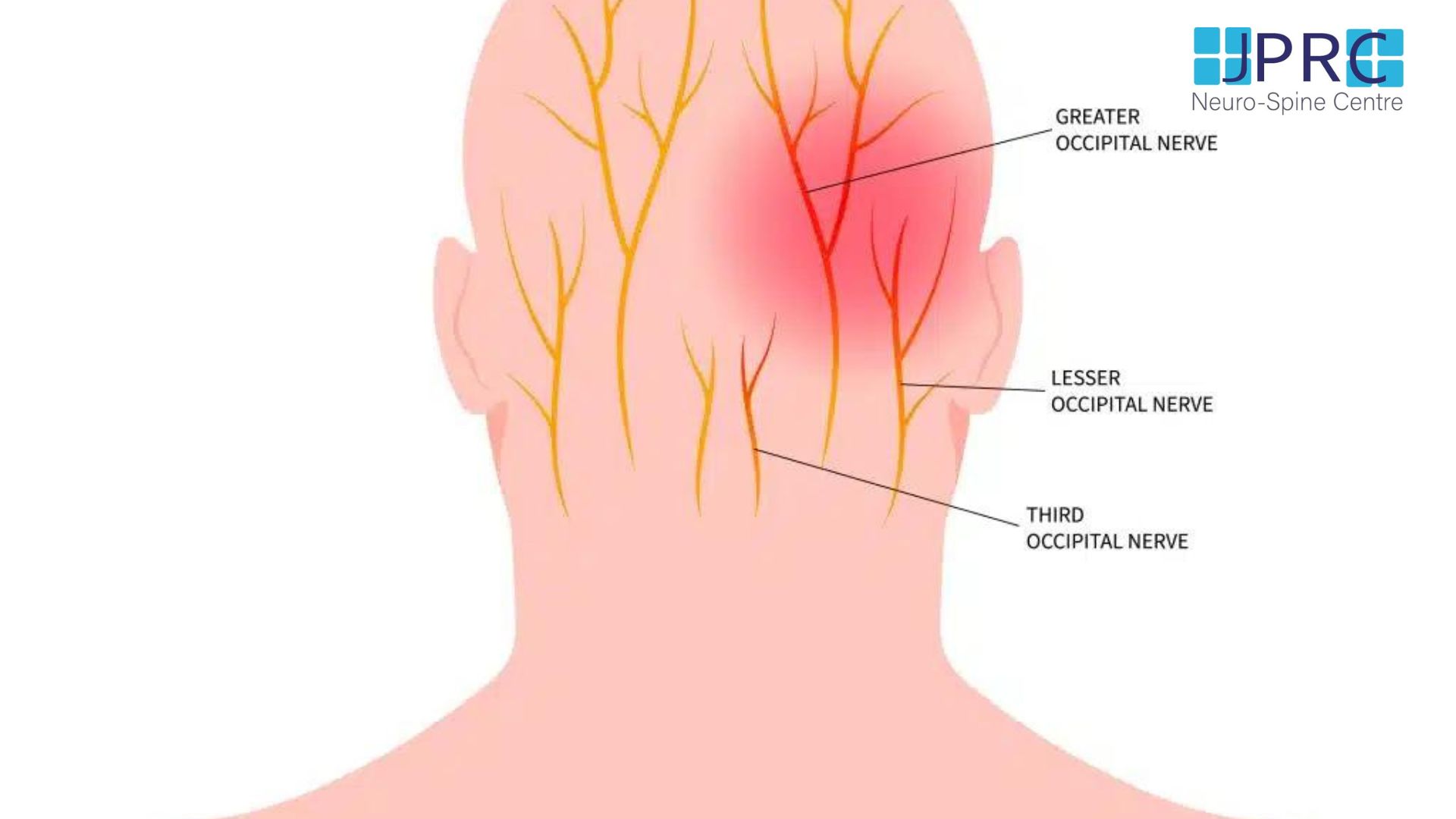
Why is chronic back pain therapy so dependent on MRIs? Chronic back pain generally entails complex soft tissue disorders. Herniated discs, spinal stenosis, muscle and ligament injuries, and nerve compression are examples. MRIs capture these soft tissues in exquisite detail, giving your doctor a complete picture of your spine.
Accuracy matters
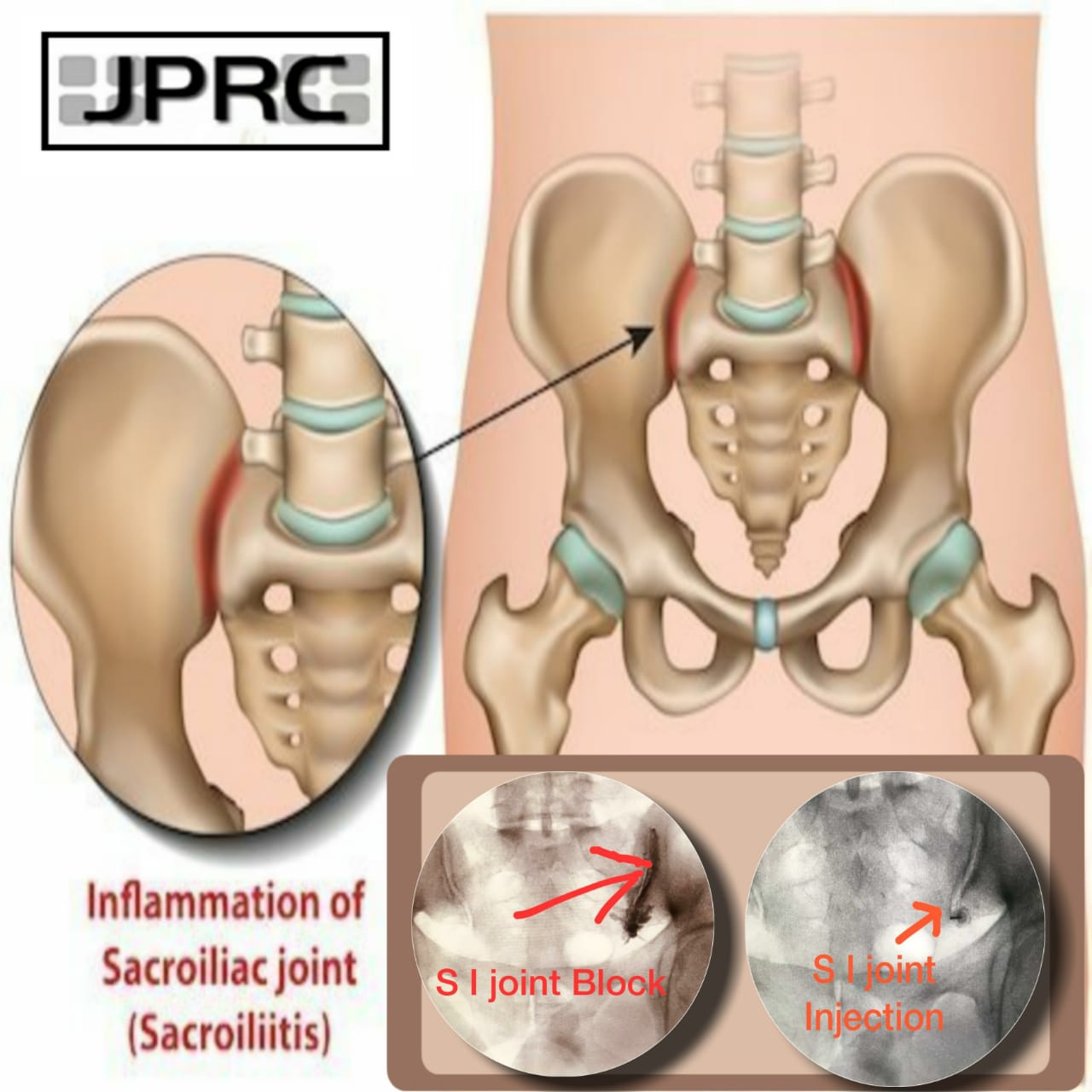
An MRI can accurately diagnose chronic back pain, which is a major benefit. MRIs can also detect conditions that X-rays miss. Spinal infections, tumors, and inflammatory illnesses may not show up on X-rays but can be spotted by an MRI.
X-rays can diagnose certain back discomfort but not chronic soft tissue problems. However, an MRI provides a complete image of bones and soft tissues, making it a useful tool in chronic back pain management. MRI scans aid people with back pain by providing a more accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
Please like, comment, and share this post if you found it useful, and don't forget to subscribe for more interesting information about medical imaging. We appreciate your attention and hope to have you back for future videos.

















































.jpg)








_Injection_Description_in_Hindi.jpg)













.jpg)







.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)








2.jpg)
3.jpg)
4.jpg)
1.jpg)
2.jpg)
5.jpg)
6.jpg)

7.jpg)
2.jpg)

8.jpg)

9.jpg)
3.jpg)

10.jpg)

11.jpg)


12.jpg)
4.jpg)