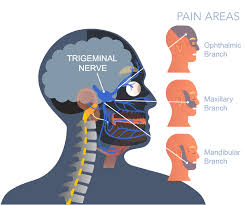
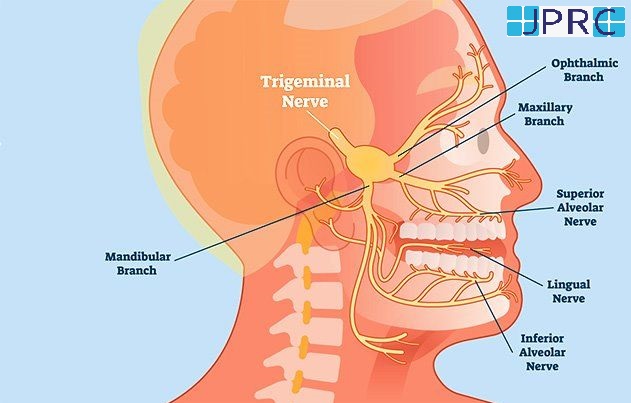
neuralgia
What to know about neuralgia.
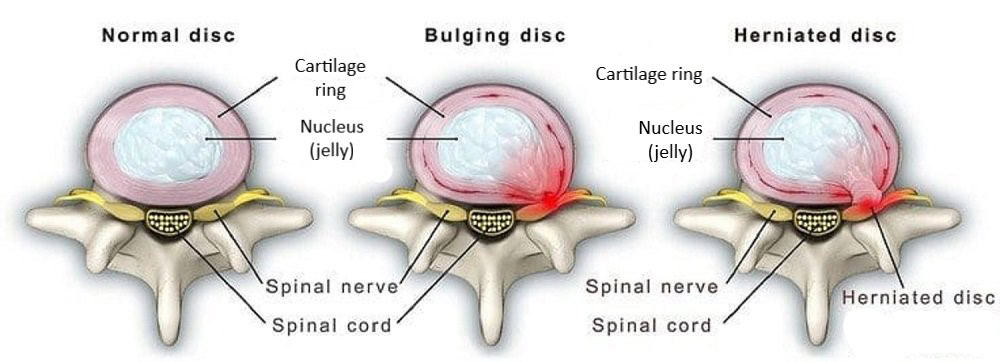
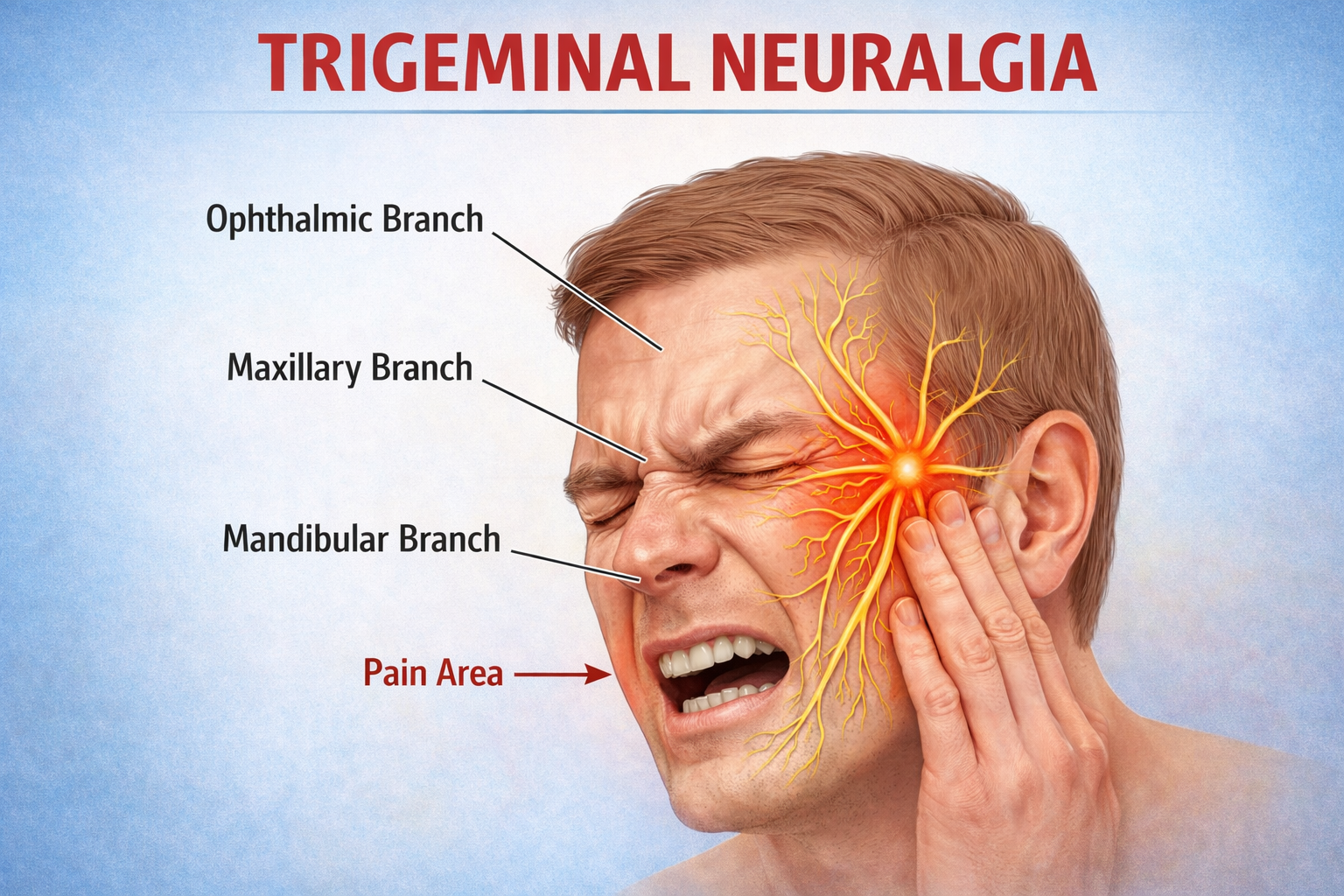
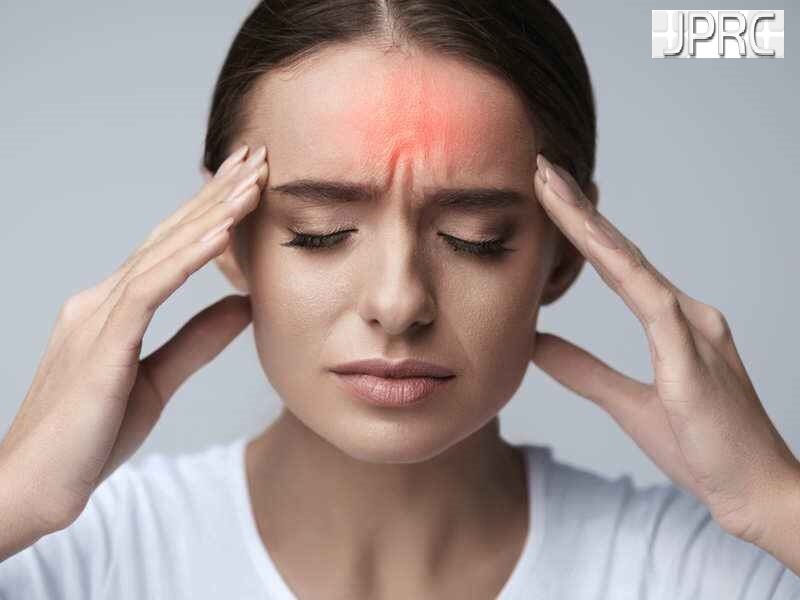
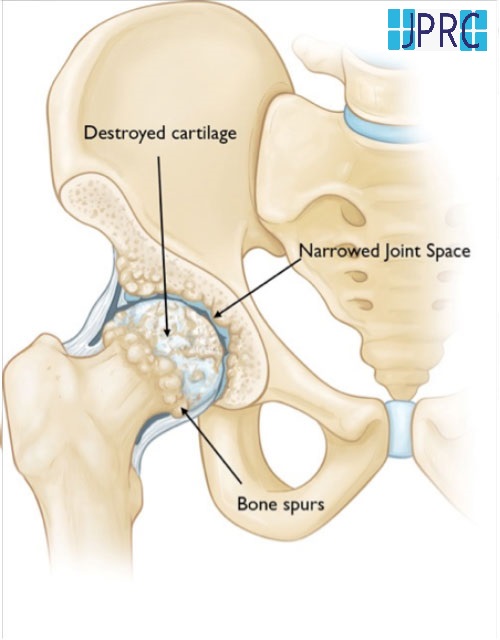
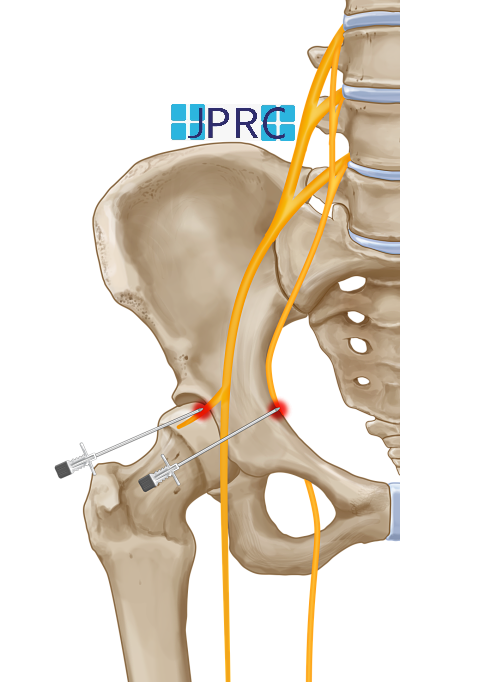
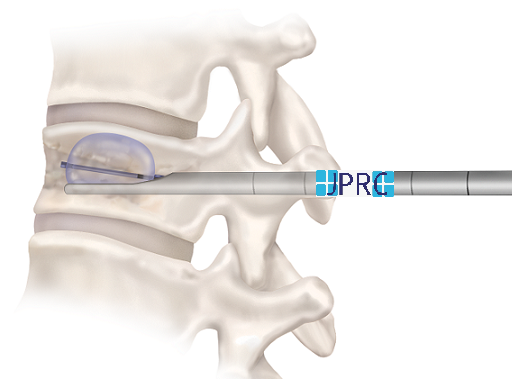
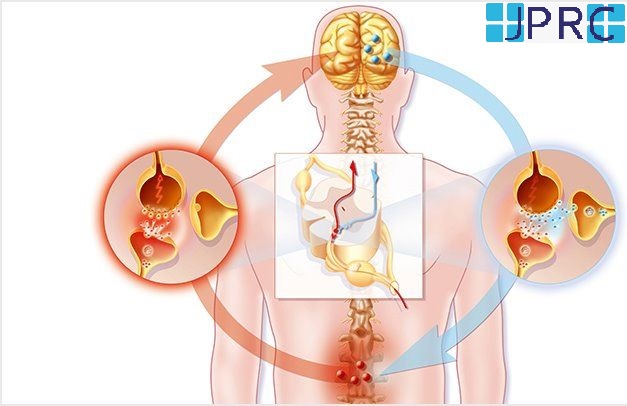
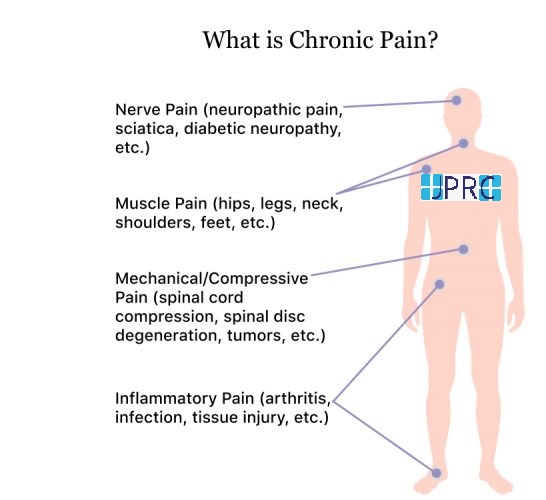
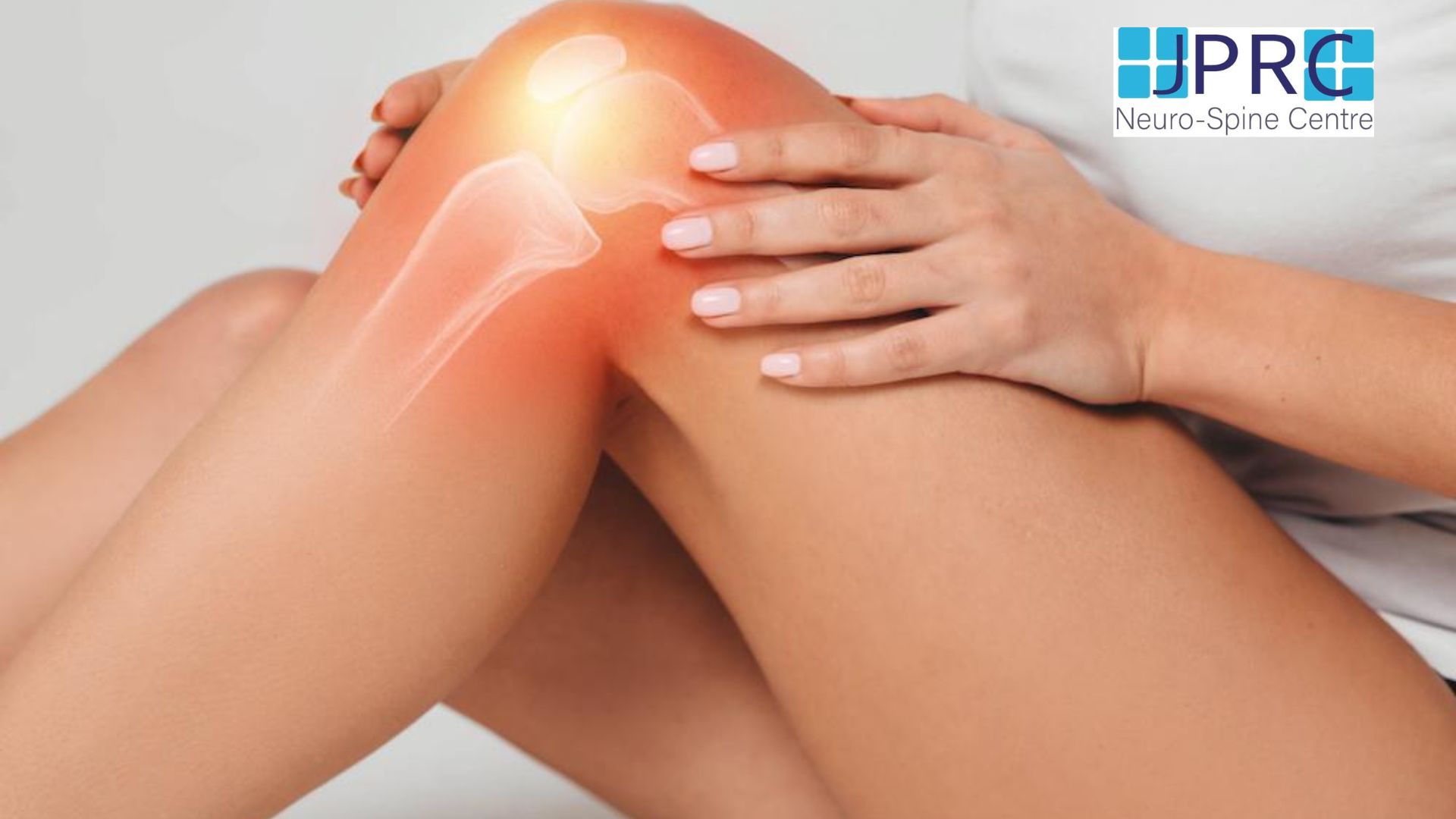
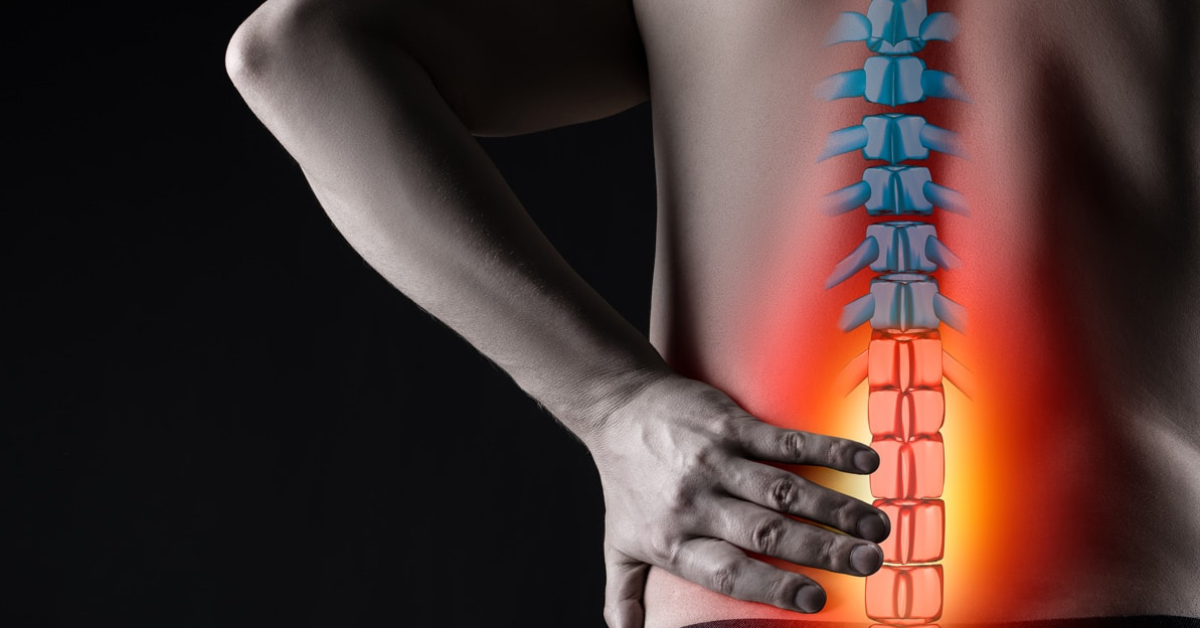
Neuralgia refers to severe, shooting pain that occurs due to a damaged or irritated nerve. Neuralgia can affect any part of the body, causing mild to severe pain. Certain medications and surgical procedures can effectively treat neuralgia.
Severe Neuralgia can interfere with a person’s ability to perform everyday activities and may impact their quality of life.
Neuralgia has many possible causes, including:
- Infections, such as Lymes, or Herpes
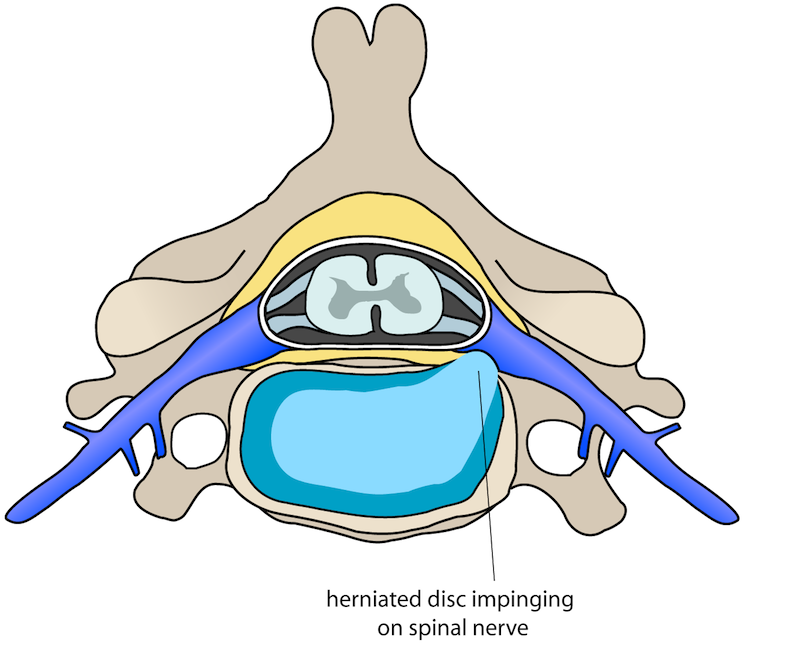
- Pressure on nerves from bones, blood vessels, or tumours
- Other medical conditions, such as kidney disease
- Diabetes
- Ageing
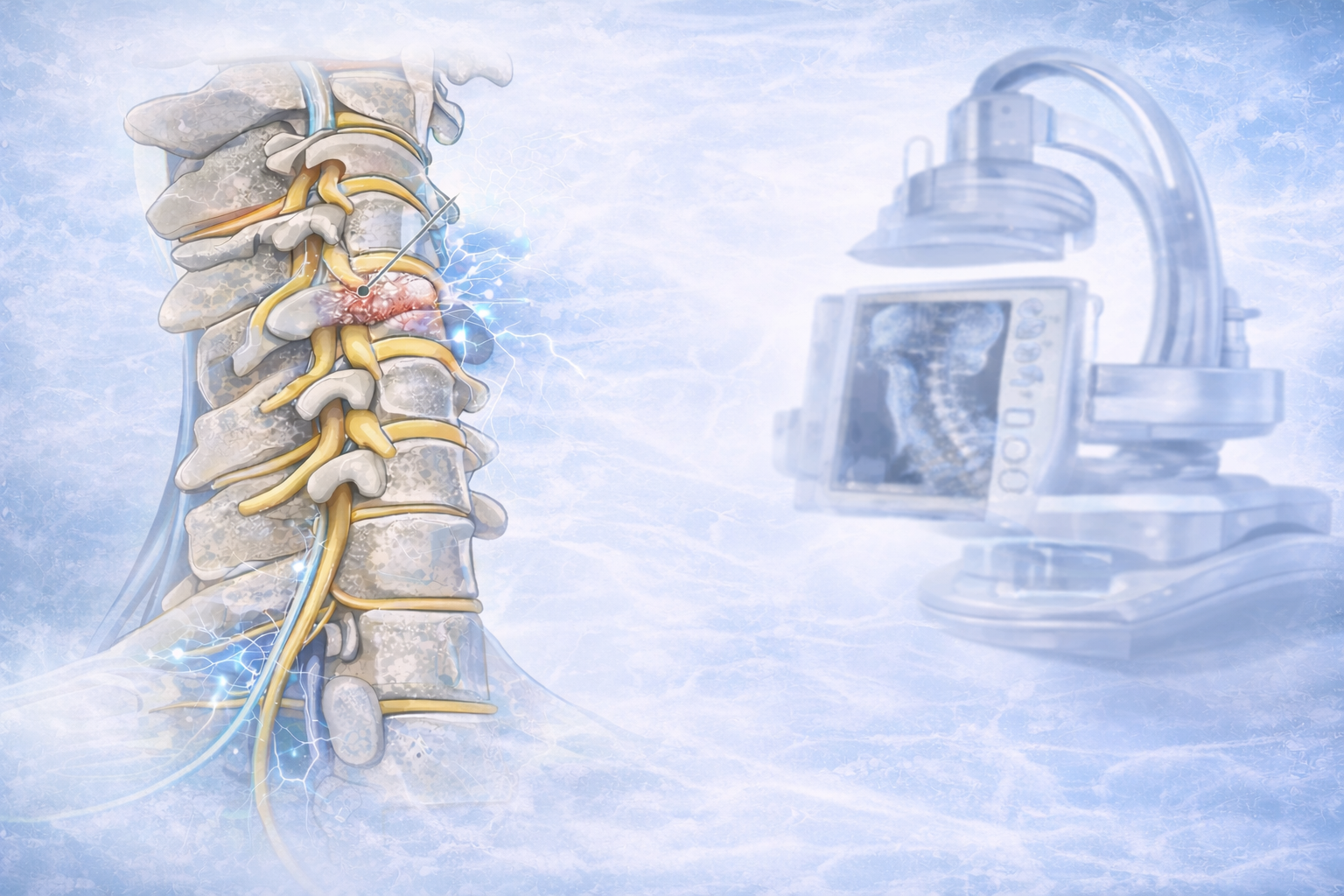
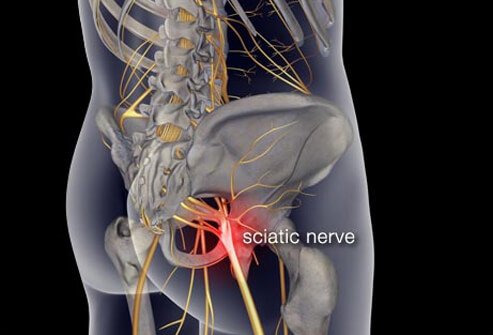
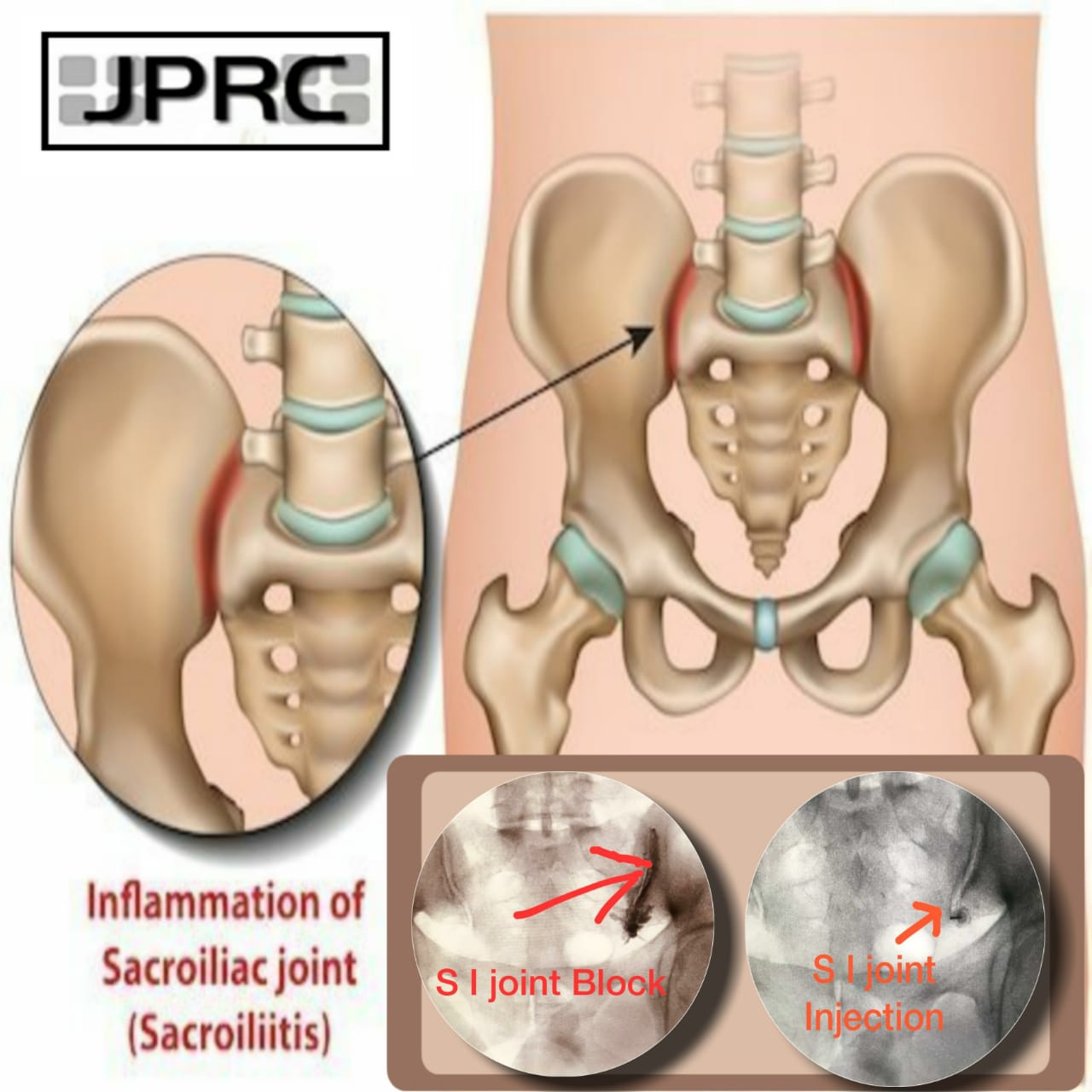
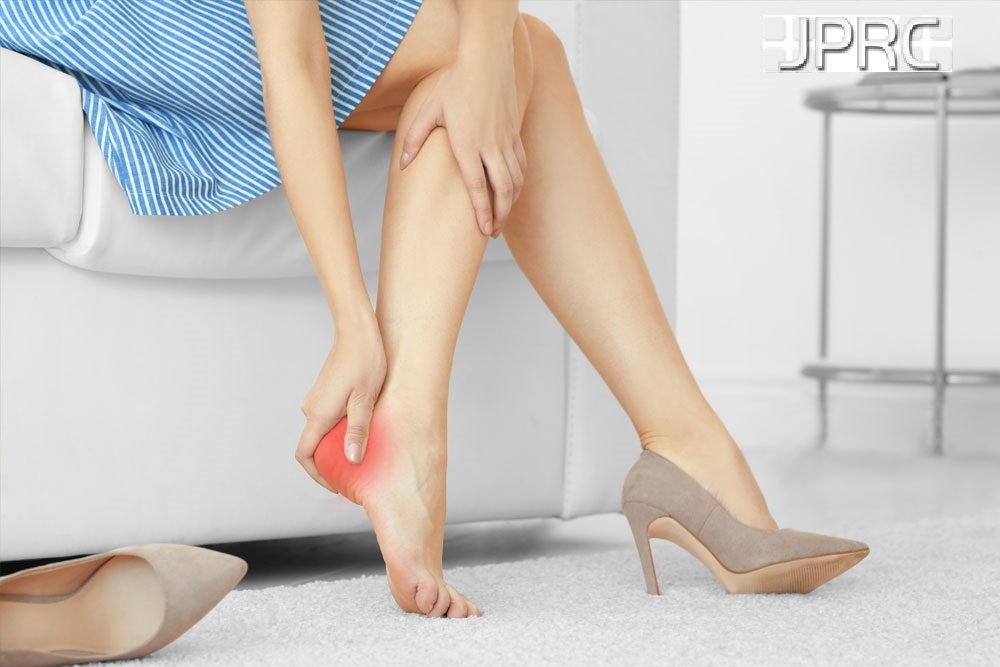
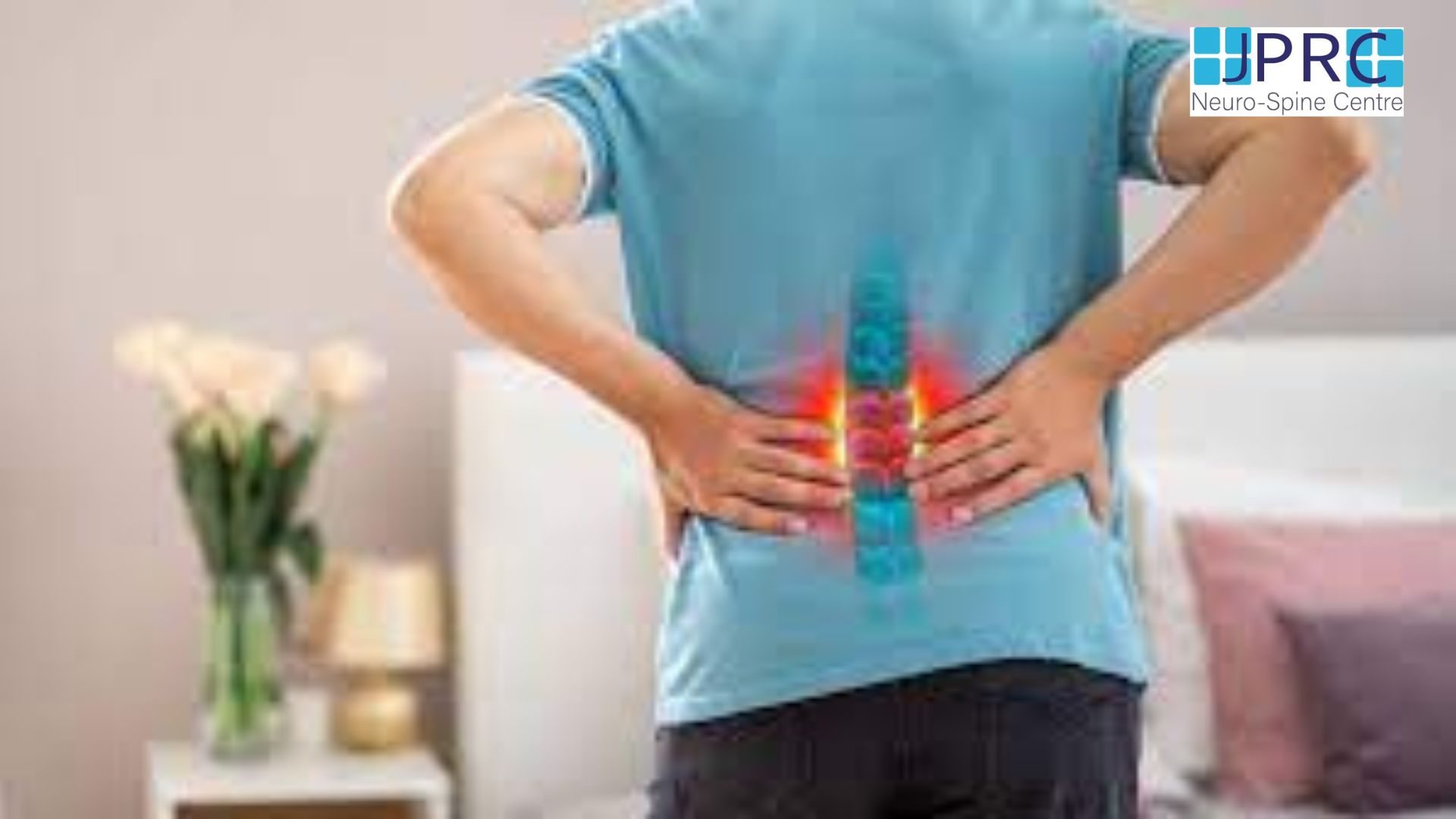
Peripheral neuralgia
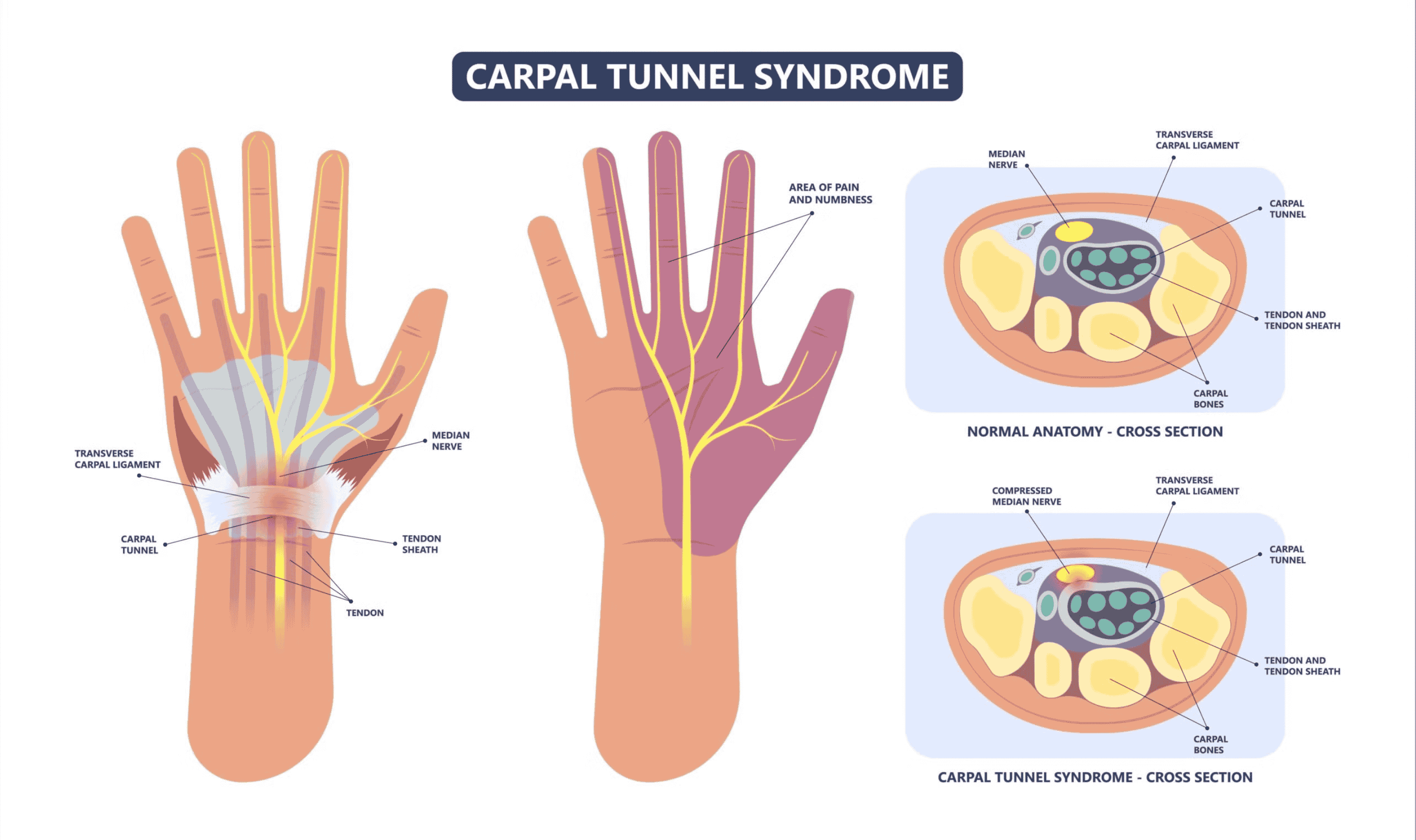
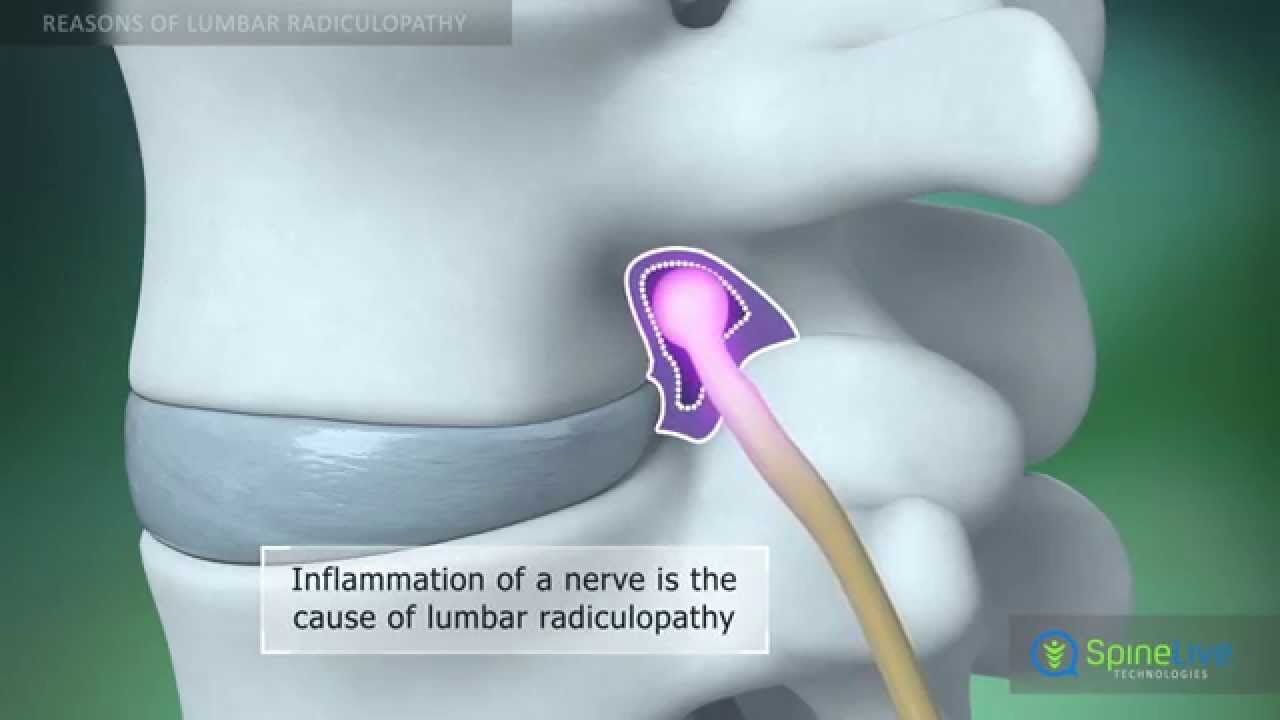
Sustaining damage to the peripheral nervous system can affect nerves that control muscle movements, transmit sensory information, and regulate internal organs.
Peripheral neuralgia can be the reason for pain in the hands, feet, arms, and legs. Other symptoms may include:
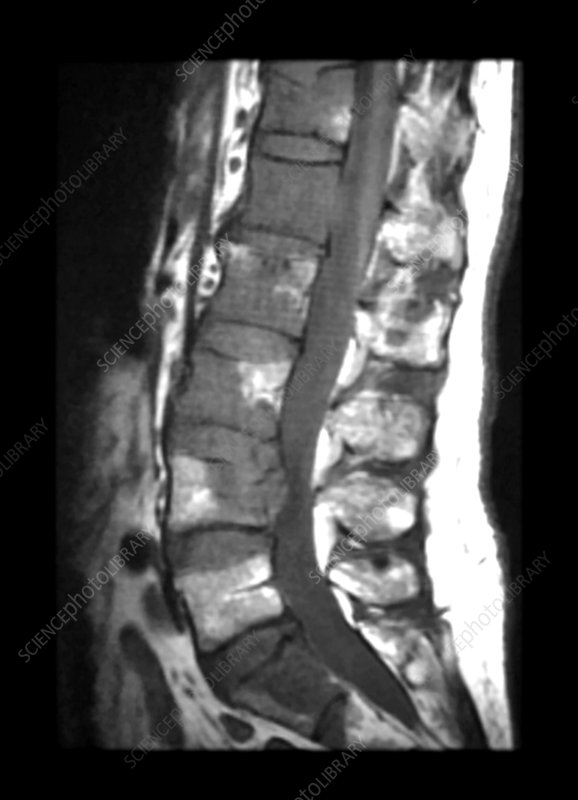
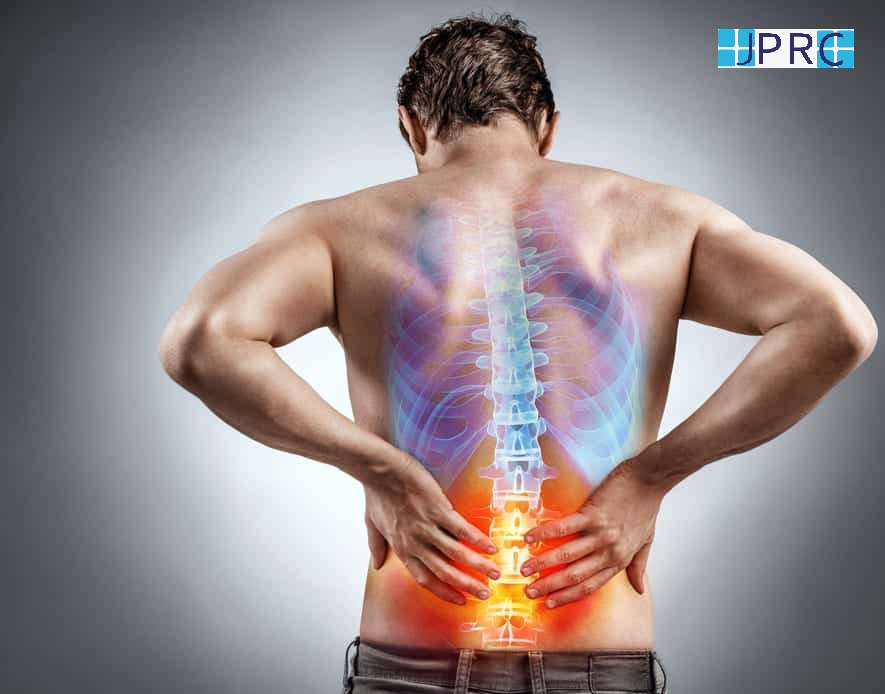
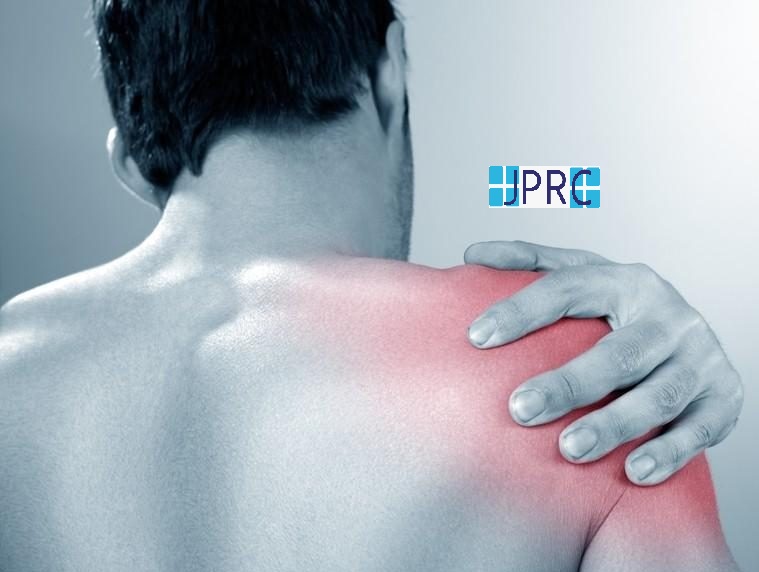
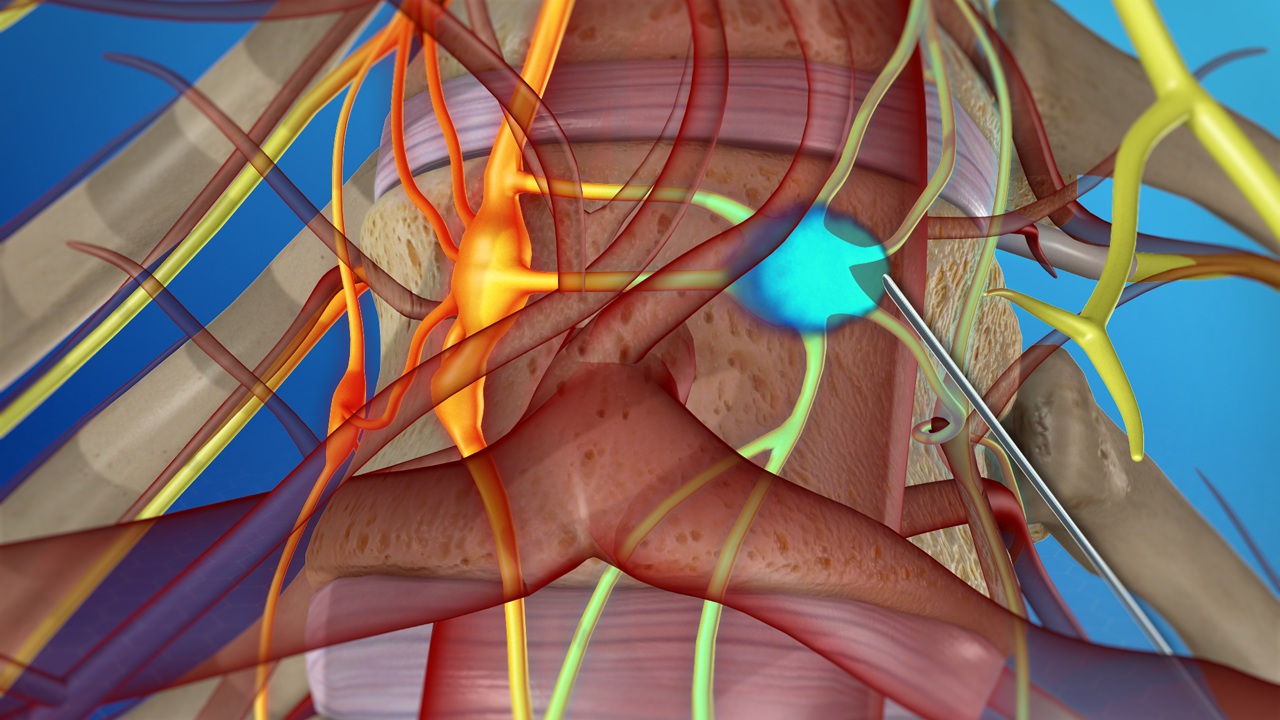
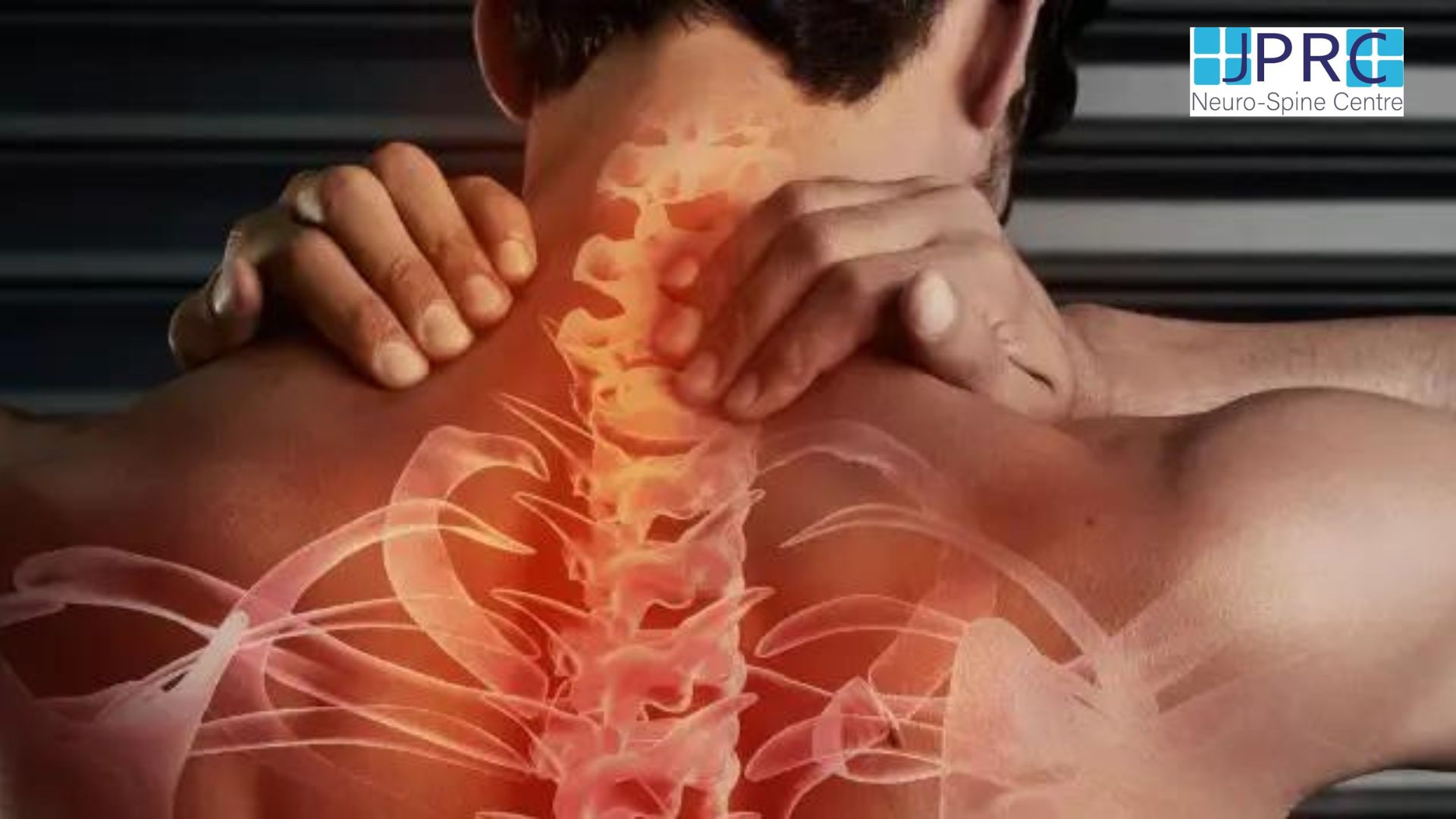
Intercostal neuralgia
Intercostal neuralgia affects the nerves that sit just below the ribs. Doctors call the muscles in this area the intercostal muscles.
Several potential factors may contribute to intercostal neuralgia, such as:
Intercostal neuralgia causes a sharp, burning pain that affects the chest wall, upper abdomen, and upper back. Certain physical movements, such as breathing, coughing, or laughing, can worsen the pain.
Additional symptoms may include:
- Involuntary muscle twitching or cramping
- Loss of coordination
- Difficulty performing complex motor tasks, such as buttoning a shirt or tying shoelaces
- Hypersensitivity to touch or temperature
- Excessive sweating
- Gastrointestinal problems
- Dysphagia-difficulty in swallowing
- Difficulty speaking
- Injuries or surgical procedures that involve the chest
- Pressure on the nerves
- Shingles or other viral infections
- Tightness or pressure that wraps around the chest
- Tingling or numbness in the upper chest or upper back
- Muscle twitching
- Loss of appetite

















































.jpg)








_Injection_Description_in_Hindi.jpg)













.jpg)







.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)








2.jpg)
3.jpg)
4.jpg)
1.jpg)
2.jpg)
5.jpg)
6.jpg)
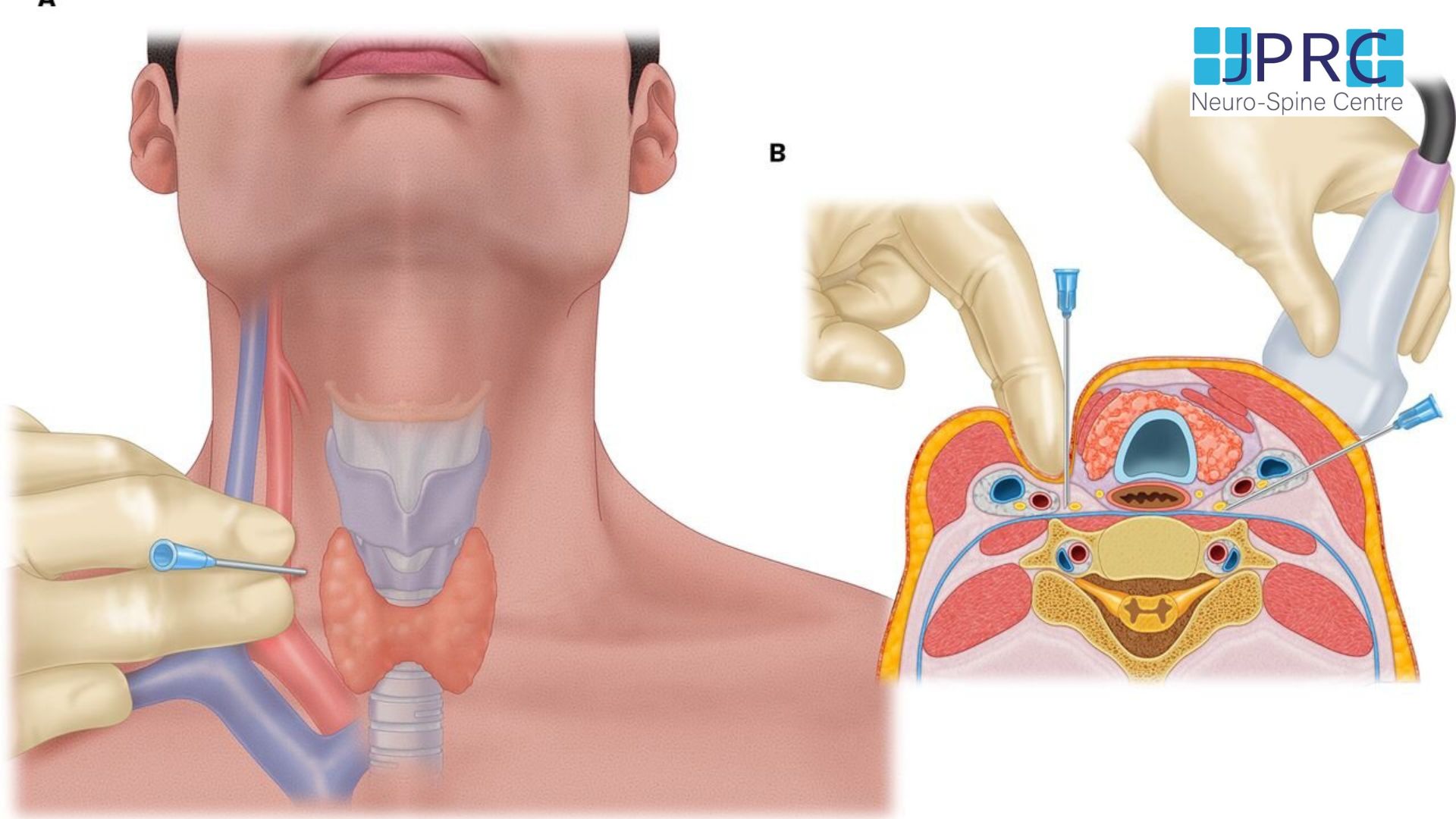

7.jpg)
2.jpg)

8.jpg)

9.jpg)
3.jpg)

10.jpg)

11.jpg)


12.jpg)
4.jpg)