slipdisc Non Surgical Treatment
A herniated disc can be a painful and frustrating situation for people with active lifestyles. If you’ve been diagnosed with a herniated disc, or if you think your symptoms may be the result of a herniated disc, you probably have questions about your condition and how best to resolve it.
What to do when Non-Surgical Treatment for a Herniated Disc doesn’t work. You can use this information to resolve doubts and to form questions for your doctor.
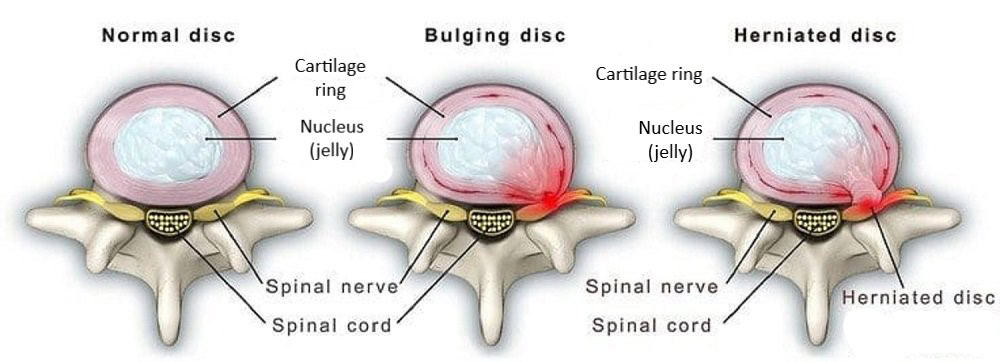
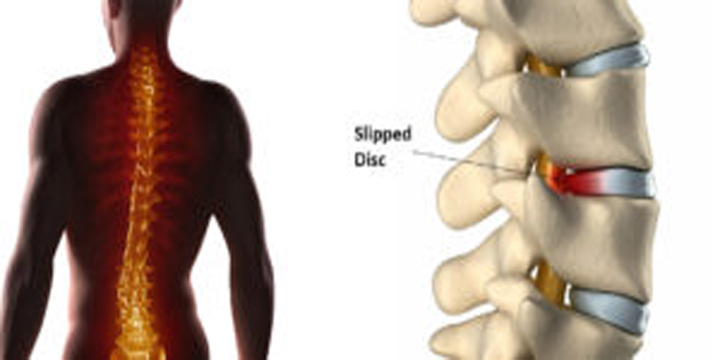
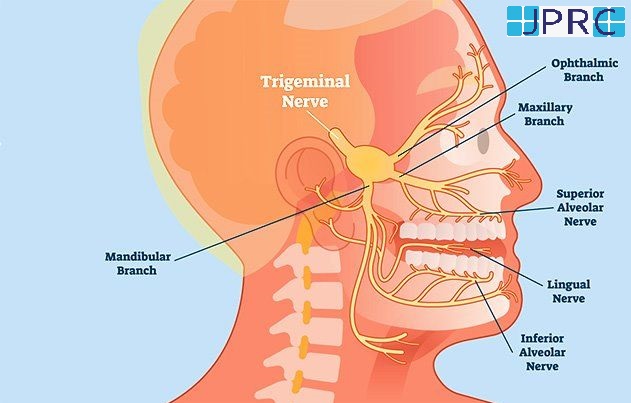
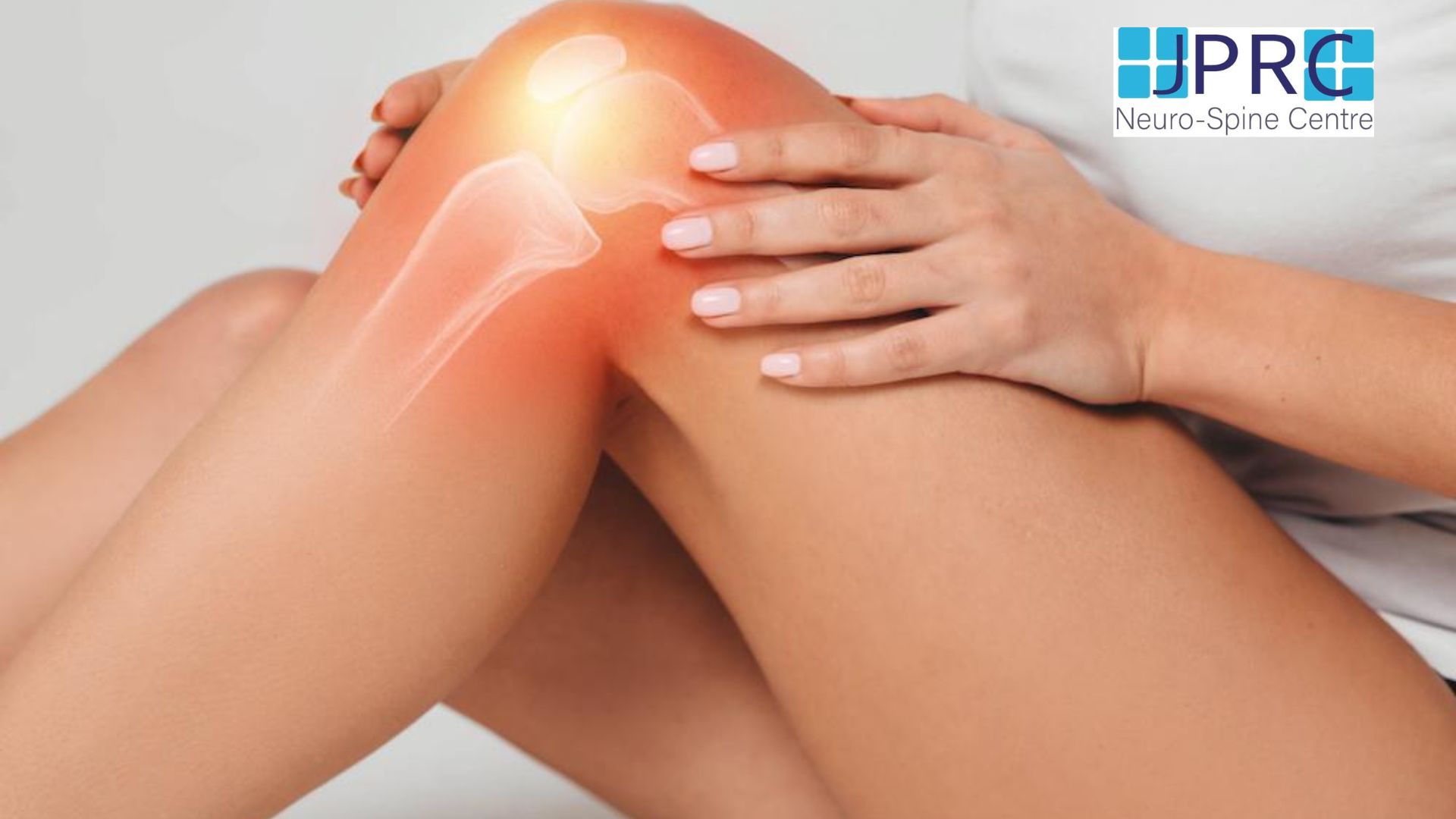
What is a Herniated Disc?
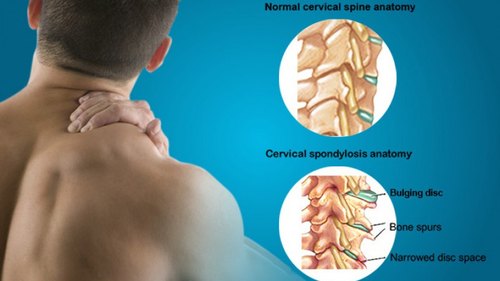
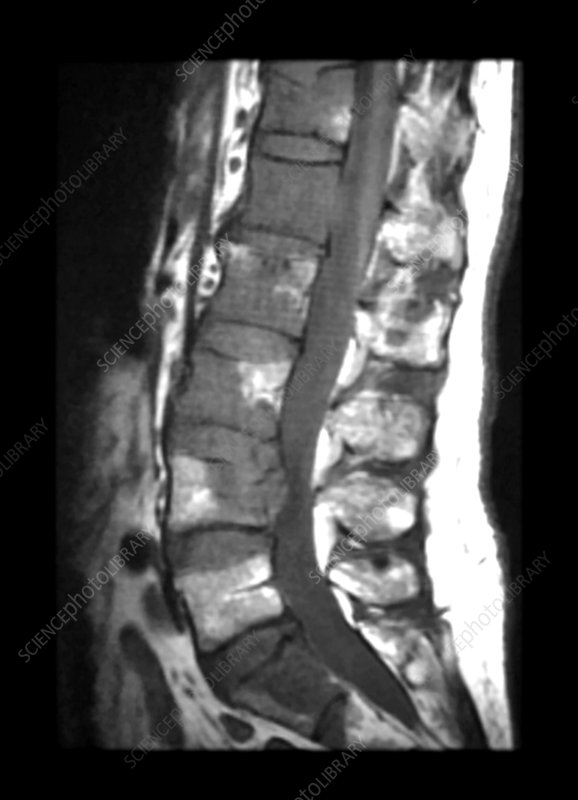
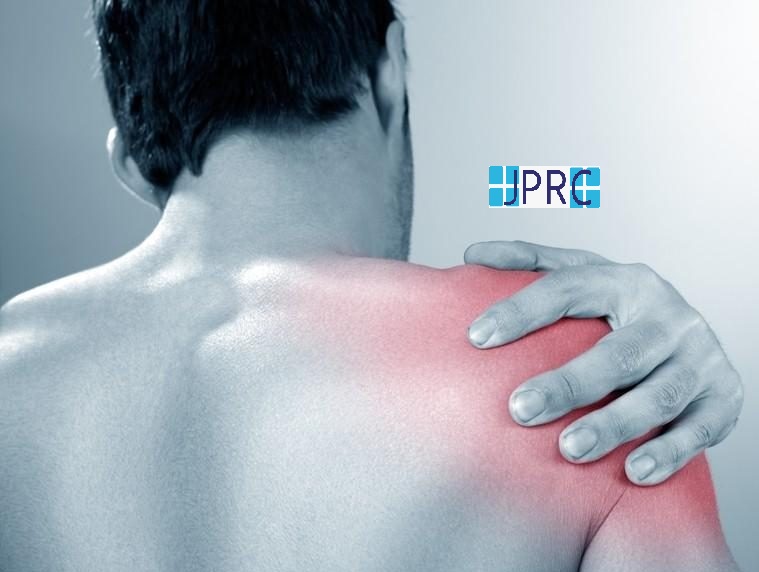
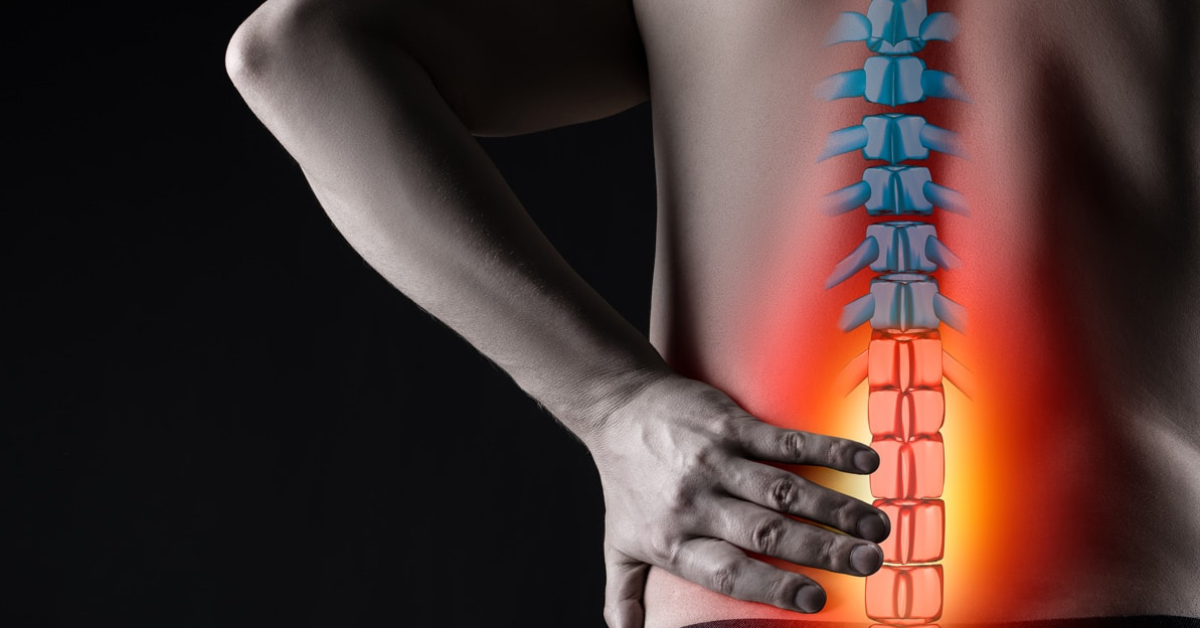
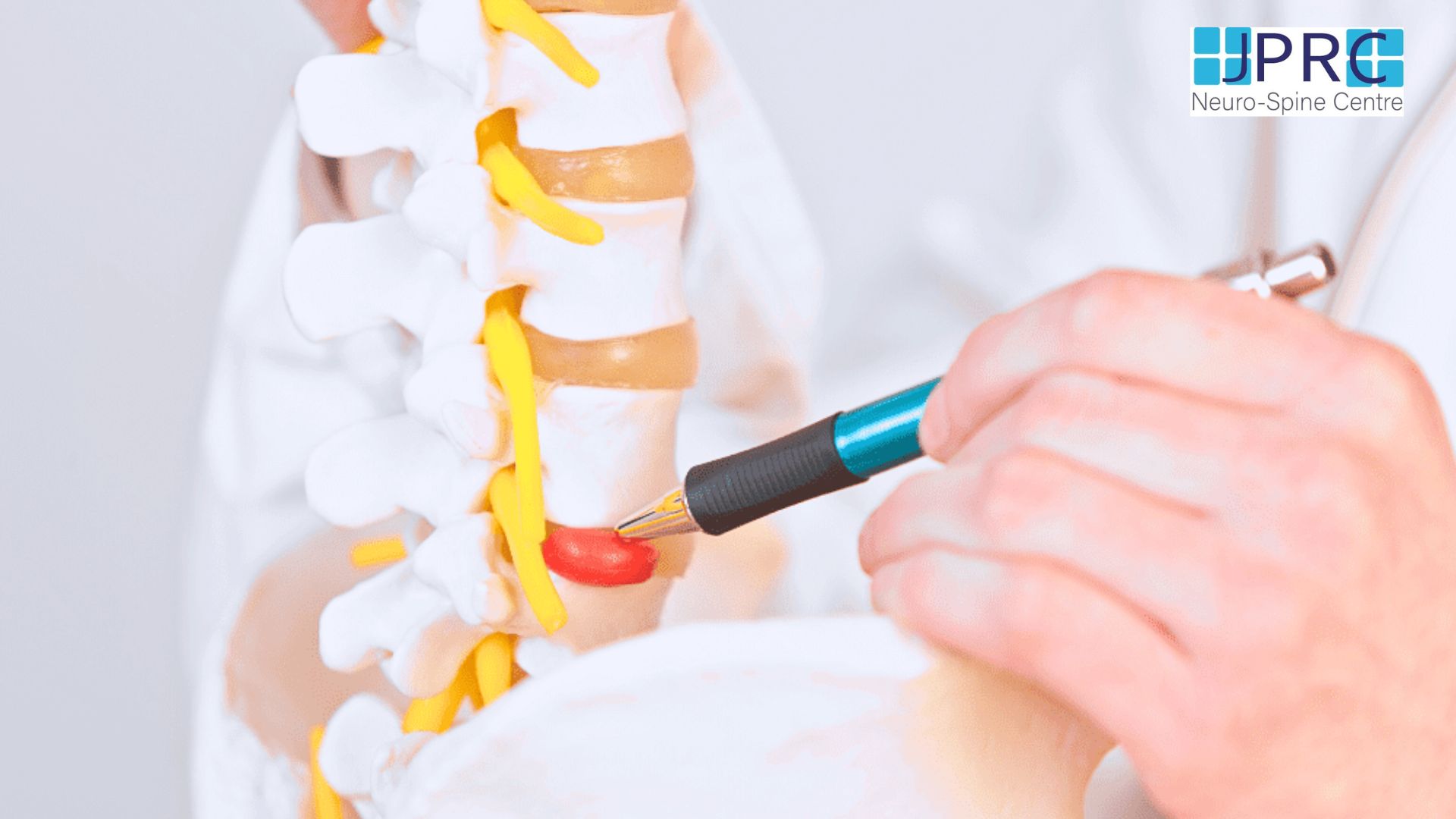
The human spine consists of a line of segments separated as classified as cervical, thoracic, lumbar regions. and cushioned by pieces of soft tissue known as vertebral discs. These discs protect the spinal cord and allow the spine to be more flexible. and function as a cushion or shock absorber. However, they are vulnerable to damage and degradation for physiological or mechanical reasons.
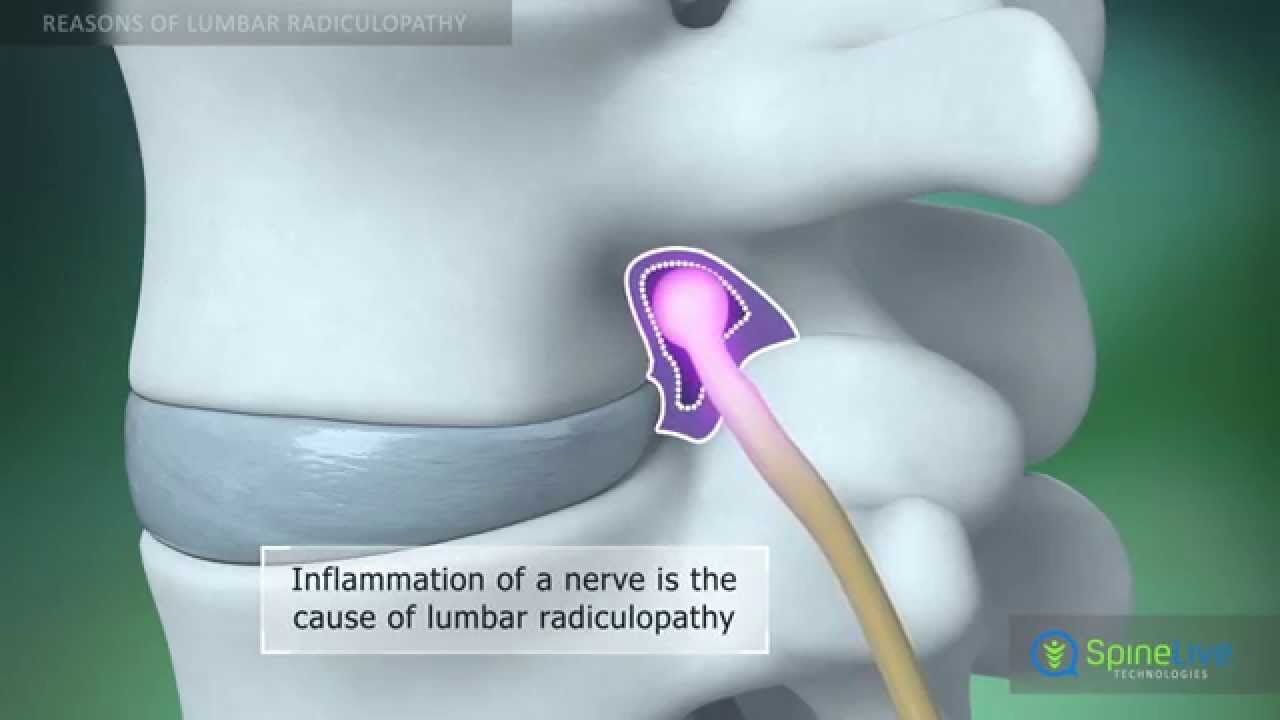
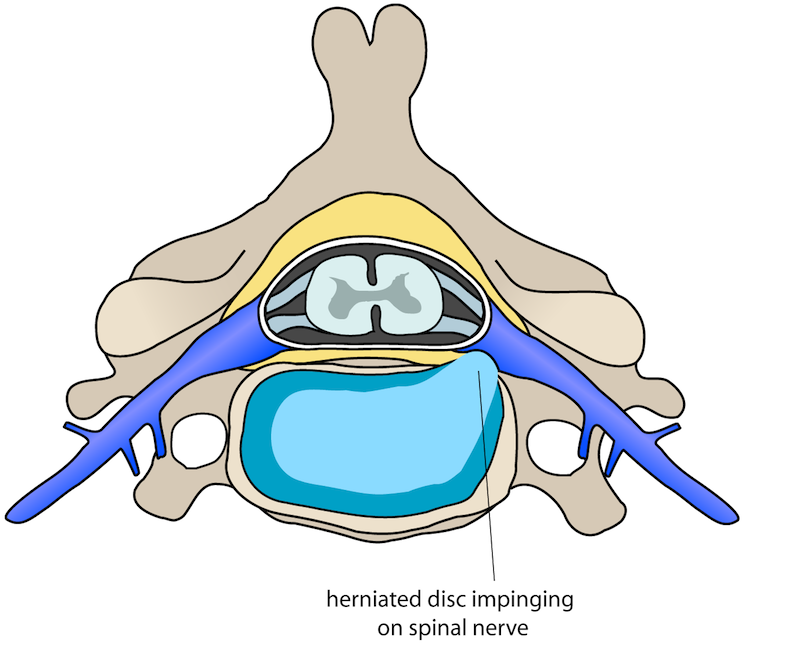
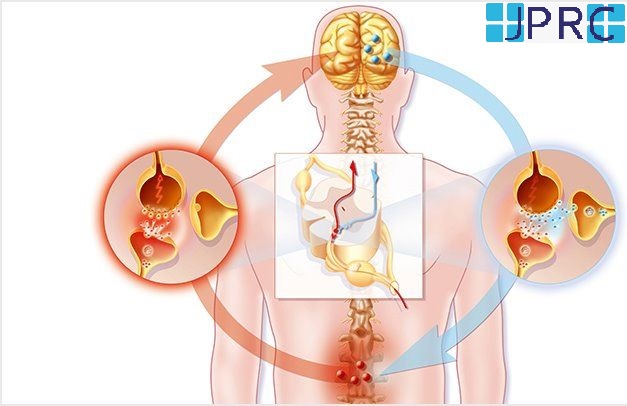
Each vertebral disc is made of a soft, jelly-like inner portion[nucleus pulposus} and a tough, protective outer portion[annulus]. Poor posture, repetitive spinal stress, spinal injury, and/or the normal wear and tear of ageing can cause the outer portion to rupture. When the outer portion of the disc ruptures, the inner portion can leak out and irritate nearby spinal nerves. This nerve irritation is responsible for the pain[chemical radiculitis] and discomfort reported by Herniated disc patients.
What are the common Non-Surgical Treatments?
Herniated discs are not necessarily a serious problem. In fact, many patients show MRI evidence of a herniated disc but report no pain or discomfort whatsoever. Nonetheless, there are many treatments available to those who do report symptoms. Here are some of the most common non-surgical treatments for a Herniated Disc.
Pain Medication
Pain medication is one of the first non-surgical treatments for a herniated disc that doctors recommend to their patients. The two most common pain medications are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroids.
NSAIDs, such as DICLOFENAC, TRAMADOL, PARACETAMOL are popular painkillers around the world, but their long-term use is often associated with cardiovascular and gastrointestinal issues. For this reason, doctors sometimes hesitate to prescribe them for persistent symptoms. Steroids are another anti-inflammatory compound often used to address back pain. They can be administered orally or epidurally, but like NSAIDs, they have shown limited benefIt
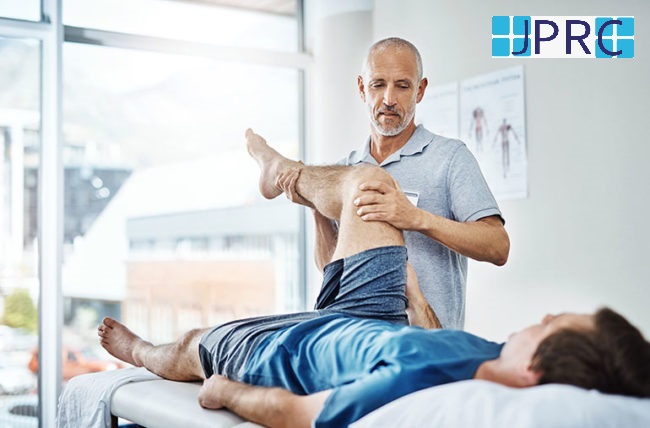
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is another common way to address pain and discomfort caused by a herniated disc. Spine issues are often due to insufficient back muscle strength. For this reason, your physician may prescribe physical therapy, which can strengthen your Back Muscles and reduce the strain on your spine. Physical therapy is typically more effective in the long term than pain medication.
Epidural Injections
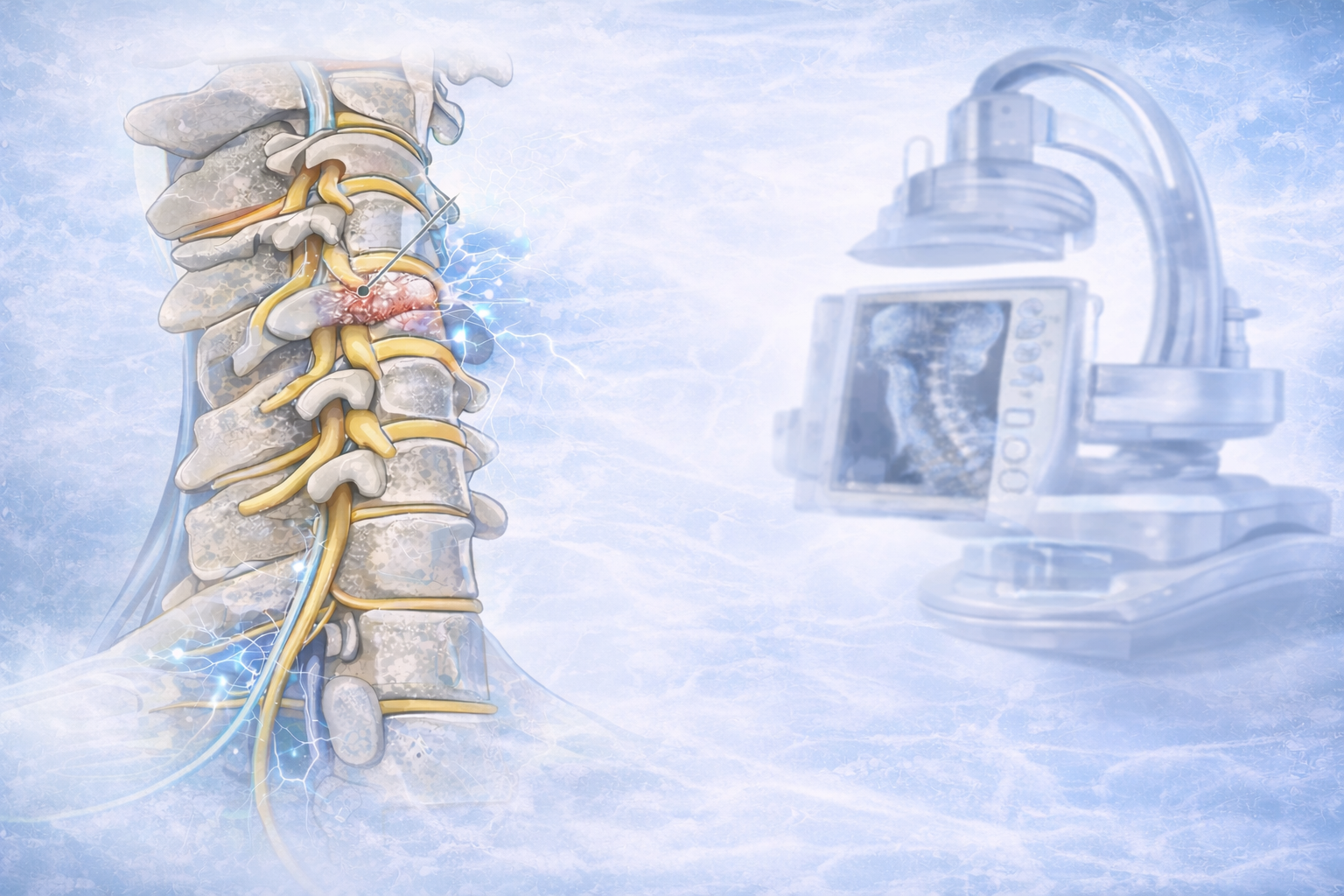
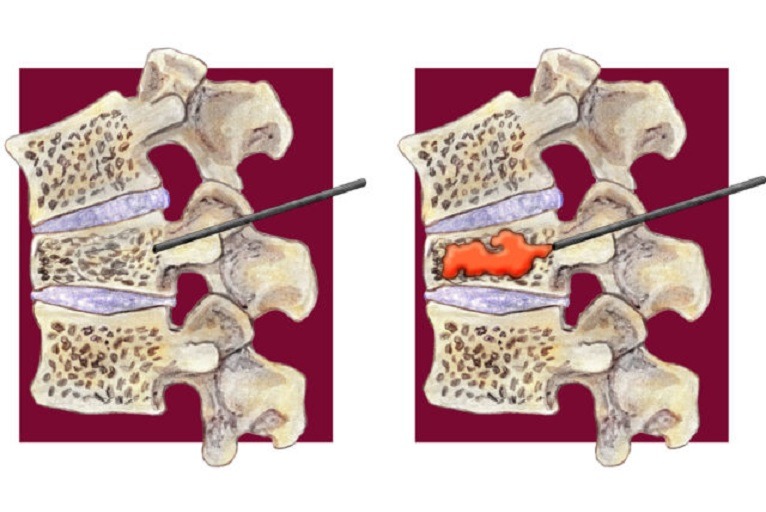
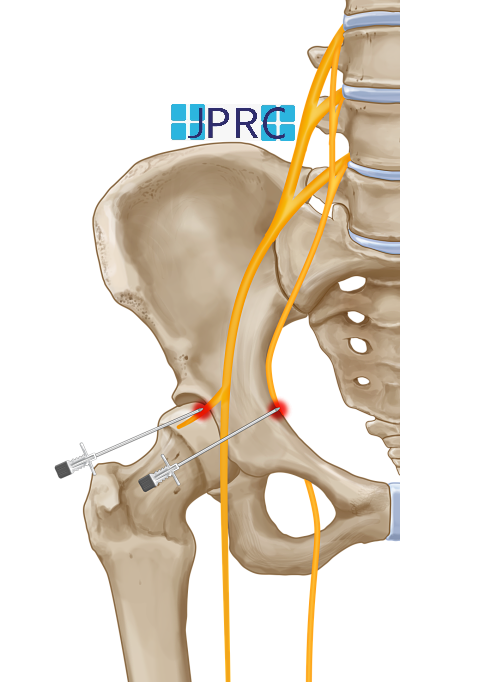
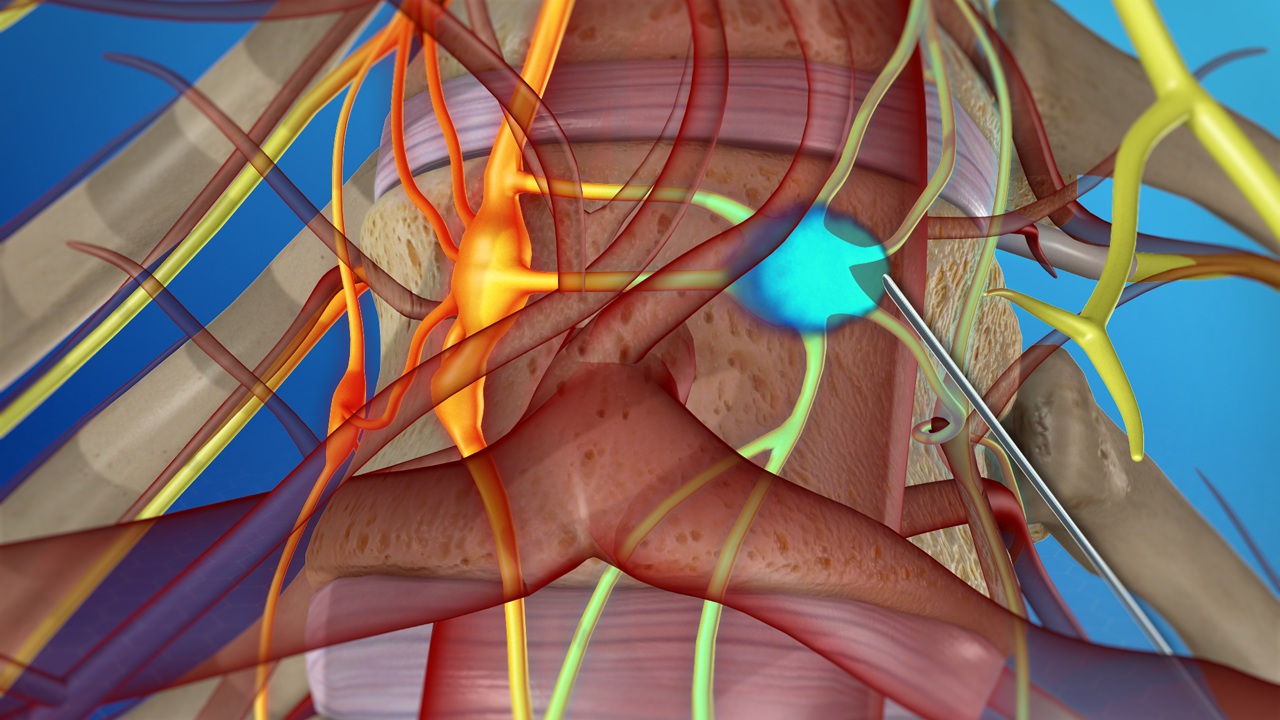
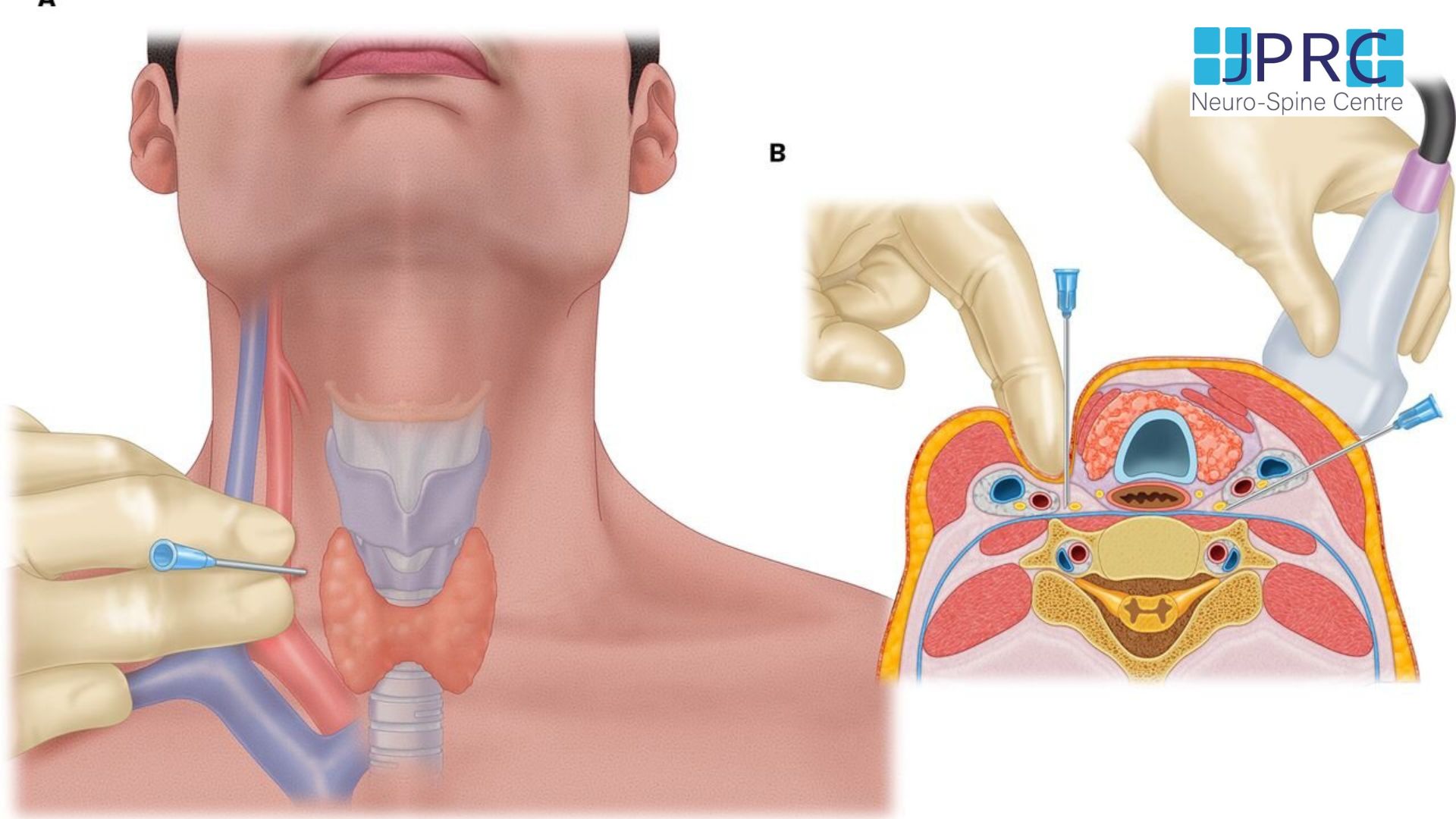
Additional treatment for a herniated disc is an epidural injection. Much of the pain and discomfort caused by a herniated disc is due to inflammation and nerve irritation. For this reason, pain physician doctors sometimes inject steroids, which are strong anti-inflammatory compounds, directly into the affected area of the spine[epidural space]. The effectiveness of epidural injections depends on the patient, and doctor who is giving the injection and they are often used by qualified pain physician.
What should you do if non-surgical options don’t work?
Many patients find relief with some combination of Pain medication, Physical therapy and Injections. However, others may wonder what to do when non-surgical treatments for a herniated disc doesn’t work. only 10 % of patients need surgical treatment, but this surgical treatment can be diverted to less scarring, less cutting-minimal invasive techniques. If you have tried conservative treatments but have not found the relief you seek, you might want to consider minimally invasive spine surgery.
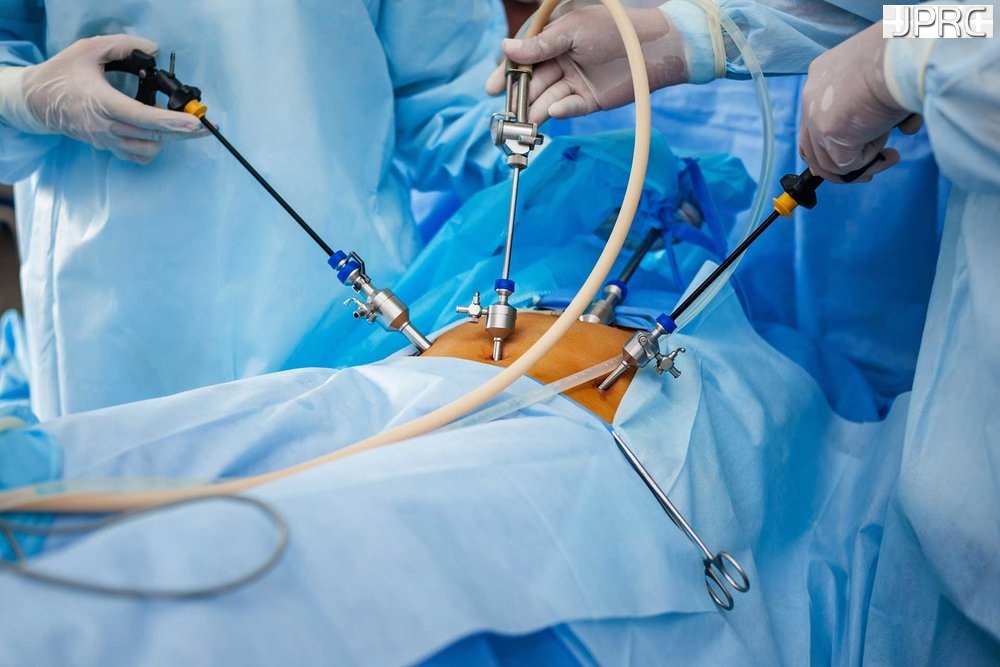
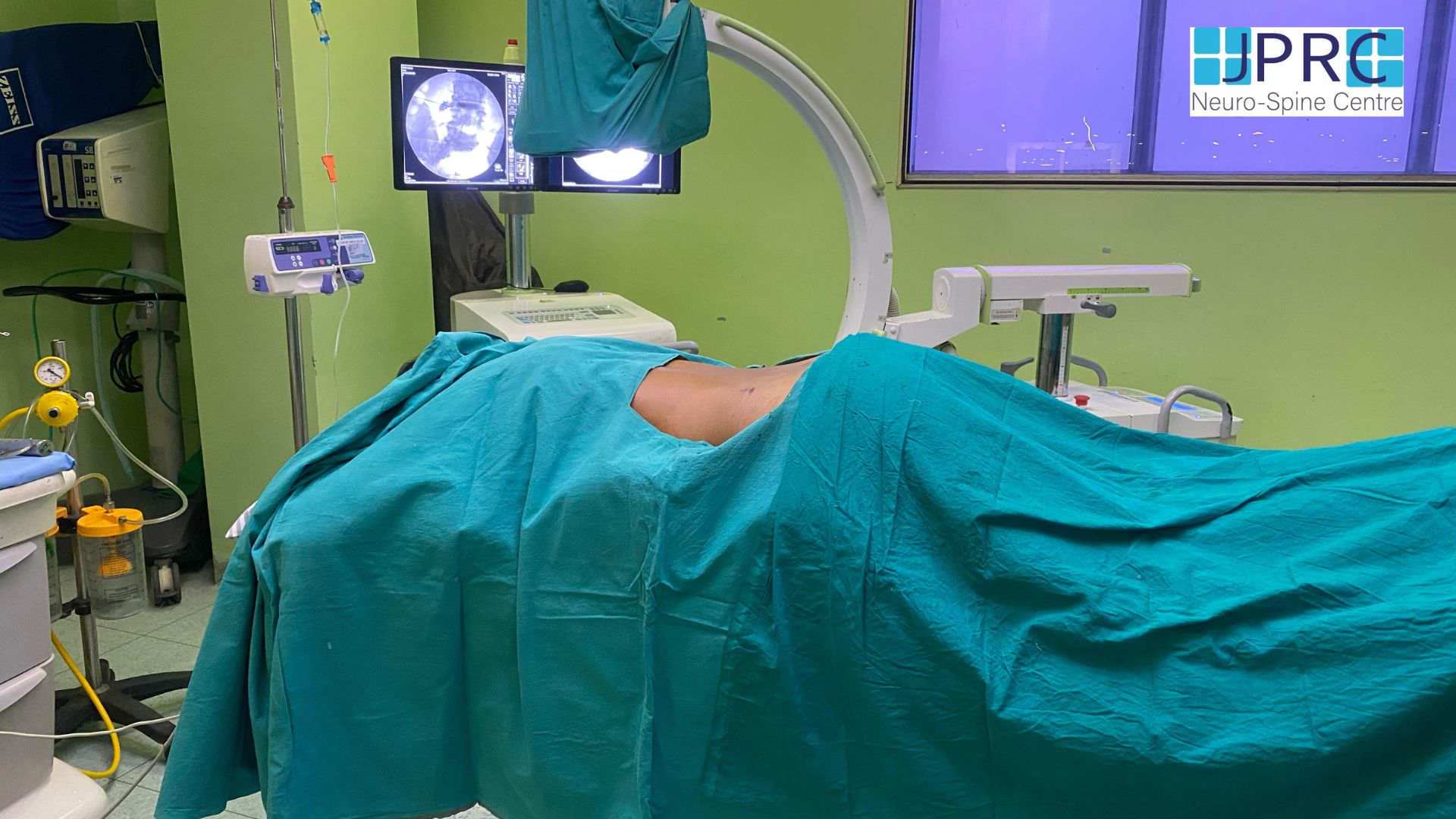
Minimally invasive spine surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery is a series of techniques used to resolve spine issues while minimizing surgical damage to healthy tissue without sacrifice your bony structure, joints or muscles. If you and your doctor have discussed your condition and have decided that minimally invasive spine surgery is the best way forward, you will first need to undergo a scan. Depending on your surgeon’s needs, an MRI, a CT scan, will be taken to help the spine surgeon locate your herniated disc and plan the best course of action.
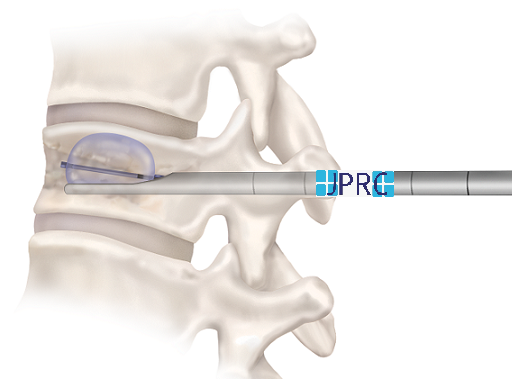
For the operation itself, you will be safely under local or general anaesthesia. The first step in minimally invasive spine surgery is to use dilation technology, sequential dilatation which allows the surgeon to move aside, rather than cut through, healthy tissue and access the herniated disc. Then, a fibre-optic tube[endoscope] will be placed near the disc to help the surgeon visualize the operation site. Once your surgeon has physical and visual access to the problematic disc, he or she will perform a Discectomy. An Endoscopic discectomy involves removing the herniated section of the disc to relieve the nearby spinal nerves from irritation and compression.
In addition to a discectomy, your surgeon may also find it necessary to perform a fusion. Sometimes removing disc material can cause the spine to lose stability your spine surgeon may insert a bone graft into the unoccupied space between your spine segments. Talk with your doctor if you have any questions about your condition or minimally invasive spine surgery.
Conclusion-
If non-surgical treatments for your herniated disc have not brought you the relief you seek, there is still a path forward. Minimally invasive spine surgery is a highly effective technique to resolve mechanical issues in the spine and bring patients back to a more active and comfortable lifestyle. You should use this guide to form questions for your pain physician so you can feel more confident and informed about the health of your spine.

















































.jpg)








_Injection_Description_in_Hindi.jpg)













.jpg)







.jpg)




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)






1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)
1.jpg)








2.jpg)
3.jpg)
4.jpg)
1.jpg)
2.jpg)
5.jpg)
6.jpg)

7.jpg)
2.jpg)

8.jpg)

9.jpg)
3.jpg)

10.jpg)

11.jpg)


12.jpg)
4.jpg)